Figure 5.
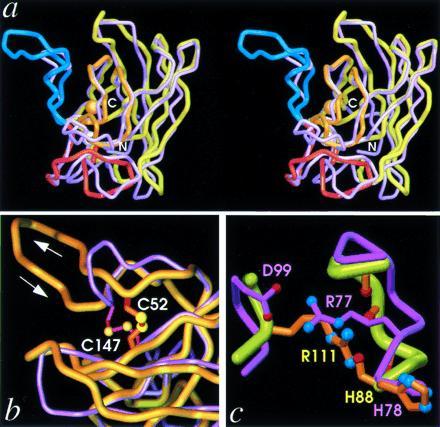
β-Barrel rearrangements. (a) Stereo pair superposition of the Cα traces of PhCuZnSOD (yellow) and BSOD (purple) subunits viewed perpendicular to the β-barrel axis (approximately 90° from Fig. 1a), showing the large insertion in PhCuZnSOD SS loop (blue, left) as well as distortions in the bottom β-sheet (center and right). The functional elements and metal ions of PhCuZnSOD are color-coded as in Fig. 1c. (b) Close-up view of SS loop in superimposed subunits, as for a. PhCuZnSOD disulfide (orange bonds with yellow spheres) Cys-52 (aligned beneath BSOD Asn-51) is located on the other side of the SS loop relative to BSOD disulfide (magenta bonds with yellow spheres) Cys-55 (both at top), while the position of PhCuZnSOD Cys-147 (BSOD Cys-144) is conserved (both below). (c) Close-up view of Zn loop in superimposed subunits, as for a, showing the functional equivalence of PhCuZnSOD Arg-111 (orange bonds and atom-colored spheres) and BSOD Arg-77 (light purple bonds and atom-colored spheres) in stabilizing the Zn loop. BSOD Arg-77 forms a salt bridge with Asp-99 (left), while PhCuZnSOD Arg-111 hydrogen bonds with four main-chain carbonyl oxygen atoms (right).
