Figure 1.
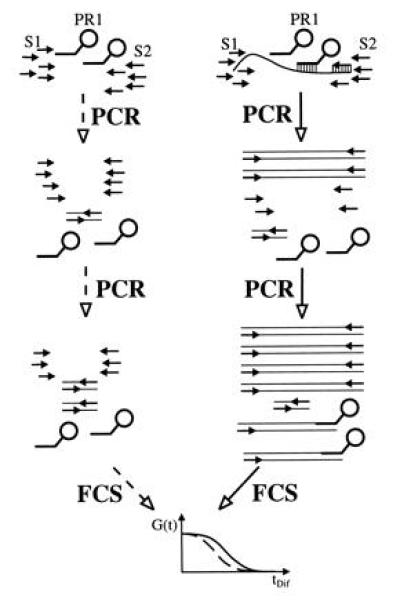
Schematic view of the APEX-FCS (amplified probe extension detected by FCS) assay in the absence (Left, dashed lines) and presence (Right, solid lines) of template. Without template, amplification primers S1 and S2 can only yield unspecific products during PCR, like primer dimers, that do not interfere with the low concentrated, fluorescent probe PR1. FCS analysis consequently reveals an unshifted fluctuation autocorrelation function G(t). With template present in the reaction mixture, PCR leads to formation of specific amplification products. Over successive PCR rounds, these increase in concentration up to a point, where hybridization with probe PR1 is efficient enough to yield extension products. The extended probe exhibits an increased diffusion time, resulting in a shifted fluorescence autocorrelation function.
