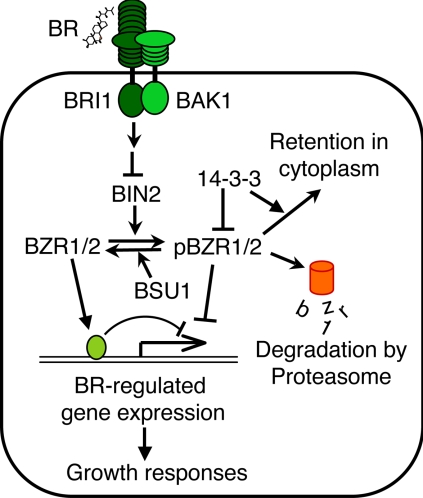
Fig. 1.
A model for the BR signaling pathway in Arabidopsis. Arrows and bars represent actions of promotion and inhibition, respectively. BR binds to the extracellular domain of the BRI1 receptor kinase to increase its kinase activity and induce dimerization with and phosphorylation of the BAK1 receptor kinase. The signal is transduced through an unknown mechanism to inhibit BIN2 kinase or activate BSU1 phosphatase, leading to dephosphorylation of BZR1 and BZR2/BES1 (denoted together as BZR1/2). BIN2 phosphorylation of BZR1/2 (pBZR1/2, phosphorylated BZR1 or BZR2/BES1) inhibits its DNA binding, targets it for proteasomal degradation, and increases its cytoplasmic retention by promoting binding to the 14-3-3 proteins. BR-induced dephosphorylation increases nuclear accumulation and DNA binding activity of BZR1 and BZR2/BES1, leading to BR-responsive gene expression and growth responses (13).