Figure 2.
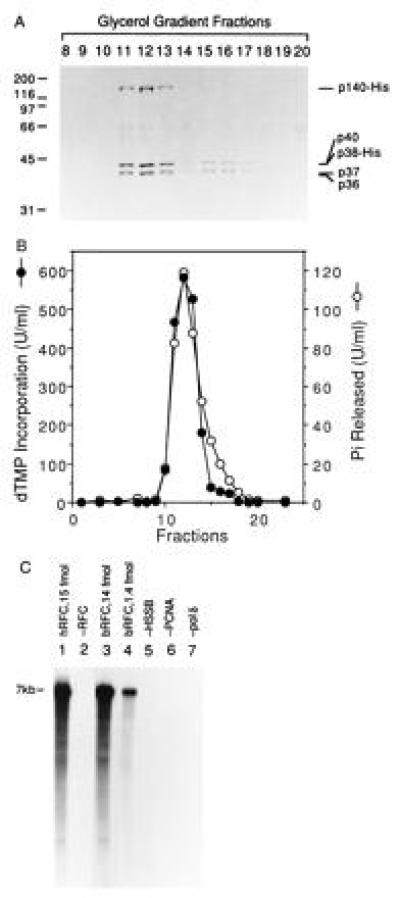
Cosedimentation of RFC-dependent DNA synthesis activity and ATPase activity through a 15–35% glycerol gradient. (A) SDS/PAGE analysis. The bRFC, eluted from a Ni-column (Fig. 1B), was further purified by two consecutive 15–35% glycerol gradient centrifugations. Following acetone precipitation and centrifugation, the pellets were analyzed by SDS/PAGE followed by Coomassie staining. The numbers at the top of the figure represent the fraction analyzed. The bands that migrated between 55–70 kDa in all lanes were artifactual. (B) RFC-dependent DNA synthesis and DNA-dependent ATPase activity. Each glycerol gradient fraction (0.5 μl after 3-fold dilution) was assayed for its ability to support DNA synthesis in the presence of a multiply primed poly(dA)4500/oligo (dT)12–18 template and ATPase activity as described. (C) RFC-dependent nucleotide incorporation using a singly primed M13 DNA template. Reactions were carried out as described using 4.4 fmol of M13 DNA template prior to separation through alkaline agarose gel followed by autoradiography. Reactions shown in lanes 1 and 2 were carried out in the presence and absence of 15 fmol of hRFC, respectively; reactions shown in lanes 3–7 were carried out with bRFC as follows: lane 3, 14 fmol of bRFC; lane 4, 1.4 fmol of bRFC; lanes 5–7, 14 fmol of bRFC in the absence or presence of HSSB, PCNA, or pol δ as indicated. Nucleotide incorporation (pmol), measured following acid precipitation and liquid scintillation counting, was as follows: lane 1, 26; lane 2, 0.4; lane 3, 24.4; lane 4, 8.8; lane 5, 2.8; lane 6, 0.48; lane 7, 0.08.
