Figure 1.
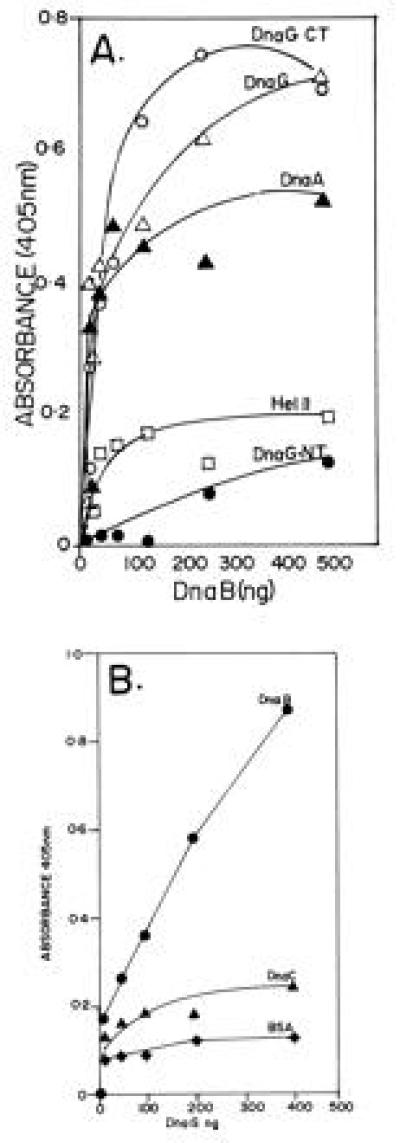
ELISA showing the interaction of DnaG primase with DnaB helicase. (A) Interaction between immobilized DnaG with DnaB in solution. Full-length DnaG and its N-terminal (DnaG-NT) and C-terminal (DnaG-CT) peptides, DnaA, and helicase II (Hel II) were immobilized on plastic surfaces of the wells of microtiter plates and were challenged with various amounts of DnaB in solution. Note that full-length DnaG and its C-terminal peptide show clear binding to DnaB. The DnaA protein, used as a positive control also binds, as expected, to DnaB. In contrast the N-terminal peptide of DnaG and helicase II (negative control) elicited low or background levels of binding signal. (B) Reciprocal binding of immobilized DnaB to DnaG in solution. DnaB, DnaC (negative control), and BSA (negative control) were immobilized on the plastic surface of microtiter plates and challenged with various amounts of DnaG in solution. Whereas DnaG readily bound to immobilized DnaB, there was only low levels of binding of DnaG to immobilized DnaC and BSA.
