Figure 4.
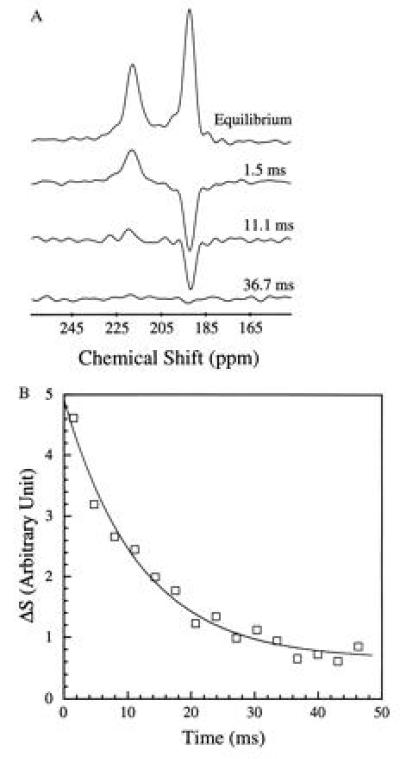
Intrinsic exchange of xenon between the two components of blood. Following an amplitude-modulated rf pulse, which selectively inverted the saline/plasma xenon signal, the recovery of the 129Xe spectrum to equilibrium was observed by using short rf pulses of small tipping angle. (A) Initial equilibrium spectrum and the time-dependent spectra following the selective inversion. The initial reduction of the RBC signal, and the rise of the saline/plasma signal, reflect the intrinsic dynamics of xenon exchanging between the plasma and the RBC. The time dependence of the signal intensities is shown in B. The time constant for the xenon exchange process is determined to be 12.0 ± 1 ms from the exponential fit shown as a solid line. The inversion exchange measurement was taken 3 s after the completion of the injection to ensure complete mixing and equilibration of the blood and the saline solution. The selective inversion pulse is 1 ms in duration with a frequency centered at the saline/plasma signal. Such a pulse also reduces the absolute signal intensities of the RBC and the plasma peaks by about 50%. A field-gradient pulse of 1 ms was applied after the inversion pulse to dephase any components of the transverse magnetization. The experiments were performed on a CMX Infinity spectrometer (Chemagnetics–Otsuka Electronics, Ft. Collins, CO) at a magnetic field of 4.3 T.
