Abstract
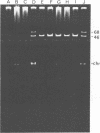
Gene transfer systems for phytopathogenic corynebacteria have not been reported previously. In this paper we describe a conjugative 46-megadalton plasmid (pDG101) found in Corynebacterium flaccumfaciens subsp. oortii CO101 that mediates resistance to arsenite, arsenate, and antimony(III). Transfer of the plasmid from CO101 to four other strains from the C. flaccumfaciens group occurred between cells immobilized on nitrocellulose filters or on agar surfaces. Transconjugant strains expressed the same levels of metal resistance as the donor strain and were able to act as donor strains in subsequent matings. The physical presence of the plasmid was detected by agarose gel electrophoresis. Arsenite-sensitive derivatives of the donor and transconjugant strains were obtained after heat treatment; these were cured of pDG101.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buck G. A., Groman N. B. Genetic elements novel for Corynebacterium diphtheriae: specialized transducing elements and transposons. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.143-152.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B. Plasmids, drug resistance, and gene transfer in the genus Streptococcus. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Sep;45(3):409–436. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.3.409-436.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J. Plasmid-determined resistance to antimicrobial drugs and toxic metal ions in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):361–409. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.361-409.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Plasmid transfer in Pediococcus spp.: intergeneric and intrageneric transfer of pIP501. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.81-89.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Götz F., Zabielski J., Philipson L., Lindberg M. DNA homology between the arsenate resistance plasmid pSX267 from Staphylococcus xylosus and the penicillinase plasmid pI258 from Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1983 Mar;9(2):126–137. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Yanagawa R. Generalized transduction in Corynebacterium renale. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):1086–1087. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.1086-1087.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kado C. I., Liu S. T. Rapid procedure for detection and isolation of large and small plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1365–1373. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1365-1373.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc D. J., Lee L. N. Rapid screening procedure for detection of plasmids in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):1112–1115. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.1112-1115.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murai N., Skoog F., Doyle M. E., Hanson R. S. Relationships between cytokinin production, presence of plasmids, and fasciation caused by strains of Corynebacterium fascians. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):619–623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaberg D. R., Clewell D. B., Glatzer L. Conjugative transfer of R-plasmids from Streptococcus faecalis to Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):204–207. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalita Z., Murphy E., Novick R. P. Penicillinase plasmids of Staphylococcus aureus: structural and evolutionary relationships. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):291–311. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Budd K., Leahy K. M., Shaw W. V., Hammond D., Novick R. P., Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H., Rosenberg H. Inducible plasmid-determined resistance to arsenate, arsenite, and antimony (III) in escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):983–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.983-996.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Silver S. Microbial transformations of metals. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:637–672. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K. Synthetic and complex media for the rapid detection of fluorescence of phytopathogenic pseudomonads: effect of the carbon source. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Nov;15(6):1523–1524. doi: 10.1128/am.15.6.1523-1524.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K. The plant pathogenic corynebacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:495–517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]