Figure 1.
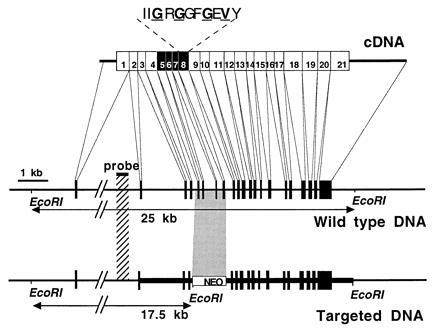
Targeted disruption of the βARK1 gene. (Top) βARK1 cDNA and location of the 21 exons. Screening of a mouse sv129 genomic library (gift from H. S. Kim, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill) with two probes obtained from either rat βARK1 or βARK2 cDNAs identified six clones of 12–15 kb. These clones were overlapping as evidenced by restriction analysis and Southern blotting (data not shown) and reconstituted a 23-kb DNA fragment. Exons 5–8 (solid boxes) were removed in the final construct for the gene inactivation. Exon 8 contains the consensus catalytic subdomain I of the protein kinases (15). The Gly and Val residues, in boldface type and underlined, are known to bind ATP. (Middle) Physical map of the βARK1 gene in the wild-type mouse. The thin line represents the introns in the genomic DNA, and solid boxes represent the exons. Intron 1 (>9 kb) is interrupted, as its actual size was not determined. The EcoRI restriction fragment length is determined on the basis of agarose gel electrophoresis and Southern blotting using the denoted probe. (Bottom) Physical map of the βARK1 gene in mouse disrupted by homologous recombination. The thick line represents the extent of the targeting construct. The counterpart of the inserted neo resistance DNA cassette is indicated by a shaded box. Solid boxes denote the exons, and an additional EcoRI site generating a 17.5-kb restriction fragment is represented.
