Figure 2.
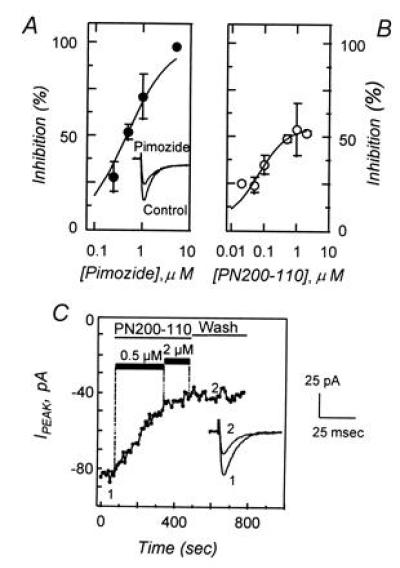
Low-voltage-activated Ca2+ currents are inhibited by pimozide and by PN200-110. (A) Dose–response relationship showing the effects of pimozide (•) on the peak Ca2+ current density after depolarization to −20 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. Data represent the mean (±SEM) response of five to eight cells and was fit to the relationship D/Dmax = (V·[C])/(Ki + [C]), where D/Dmax is the proportion of current density remaining after pimozide treatment, [C] is pimozide concentration, V is the maximum inhibition, and Ki is the inhibitory constant. In this data set V and Ki were determined to be 100% and 467 nM, respectively. (Inset) Comparison of control Ca2+ current and currents after treatment with 1 μM pimozide. (B) Dose–response relationship showing the effects of PN200-110 (○) on the peak Ca2+ current density, determined under conditions similar to those in A, with derived values of V = 53% and Ki = 39 nM. Data are obtained from one to six cells. (C) Peak Ca2+ current during repetitive depolarizations to −20 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. Depolarizations (100 msec) were provided at a frequency of 0.2 Hz. Control currents were recorded, PN200-110 was introduced by perfusion (0.5 and 2 μM; solid bars), and peak currents were recorded for several minutes. Recovery was followed for 5 min after removal of PN200-110. Representative Ca2+ current traces are illustrated before (point 1) and after (point 2) PN200-110 treatment. Scale bars for current traces are shown on the right.
