Figure 3.
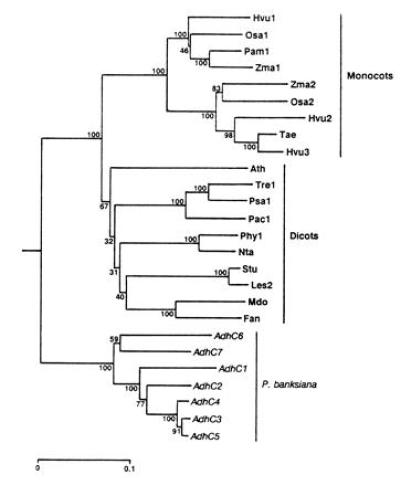
Phylogeny of Adh cDNA sequences inferred by the neighbor-joining method (26) from Jukes–Cantor distances (27) and rooted using human Adh χ (GenBank accession no. M30471M30471). Numbers represent the relative support for groupings based upon 1000 bootstrap trees and the scale bar represents 0.1 substitutions per site. The angiosperm genes included are Arabidopsis thaliana Adh (Ath; GenBank accession no. M12196M12196); Fragaria ananassa Adh (Fan; X15588X15588); Hordeum vulgare Adh1 (Hvu1; X07774X07774), Adh2 (Hvu2; X12733X12733), and Adh3 (Hvu3; X12734X12734); Lycopersicon esculentum Adh2 (Les2; M86724M86724); Malus domestica Adh (Mdo; Z48234Z48234); Nicotiana tabacum Adh (Nta; X81853X81853); Oryza sativa Adh1 (Osa1; X16296X16296) and Adh2 (Osa2; X16297X16297); Phaseolus acutifolius Adh1-F (Pac1; Z23170Z23170); Pennisetum americanum Adh1-S (Pam1; X16547X16547); Petunia hybrida Adh1 (Phy1; X54106X54106); Pisum sativum Adh1 (Psa1; X06281X06281); Solanum tuberosum Adh (Stu; X53242X53242); Trifolium repens Adh1 (Tre1; X14826X14826); Triticum aestivum Adh (Tae; ref. 37); and Zea mays Adh1-S (Zma1; X04049X04049) and Adh2 (Zma2; X01965X01965).
