Abstract
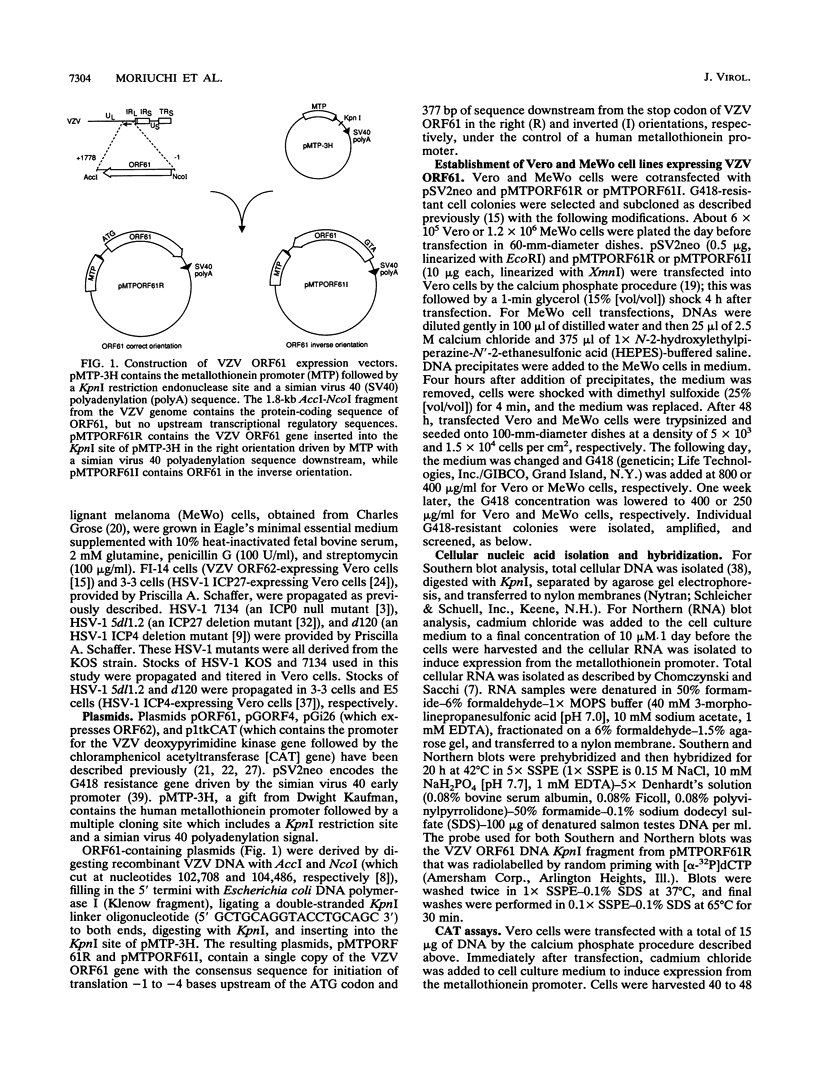
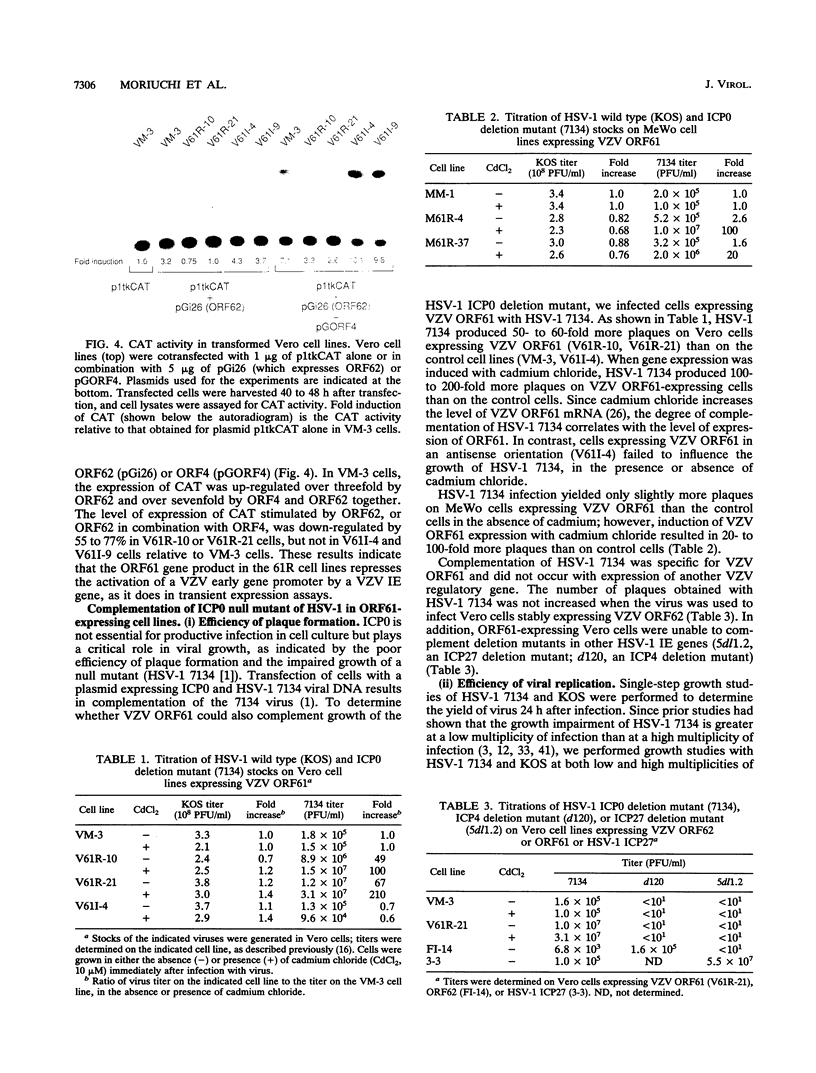
The varicella-zoster virus (VZV) open reading frame 61 (ORF61) protein is thought to be the homolog of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) ICP0, based on gene location and limited amino acid homology. However, HSV-1 ICP0 trans activates HSV-1 genes, while VZV ORF61 protein trans represses the function of VZV trans activators on VZV promoters in transient expression assays. To investigate the functional relatedness of HSV-1 ICP0 and VZV ORF61 protein, we established Vero and MeWo cell lines which stably express VZV ORF61 under the control of a metallothionein promoter and performed complementation studies with an HSV-1 ICP0 deletion mutant (7134). Mutant 7134 is impaired for plaque formation and replication at a low multiplicity of infection in cell culture, but these defects were complemented by up to 200-fold in Vero cell lines expressing VZV ORF61. Likewise, the efficiency of plaque formation was improved by up to 100-fold in MeWo cell lines expressing VZV ORF61. A cell line expressing another VZV immediate-early gene product (ORF62) was unable to complement mutant 7134. HSV-1 mutants which are deleted for other HSV-1 immediate-early gene products (ICP4, ICP27) were unable to grow in VZV ORF61-expressing cell lines. These results indicate that, despite marked differences in their sequences and in effects on their cognate promoters in transient expression assays, VZV ORF61 protein is the functional homolog of HSV-1 ICP0.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cai W. Z., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 plays a critical role in the de novo synthesis of infectious virus following transfection of viral DNA. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4579–4589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4579-4589.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W., Schaffer P. A. A cellular function can enhance gene expression and plating efficiency of a mutant defective in the gene for ICP0, a transactivating protein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4078–4090. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4078-4090.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0 regulates expression of immediate-early, early, and late genes in productively infected cells. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2904–2915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2904-2915.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. X., Zhu X. X., Silverstein S. Mutational analysis of the sequence encoding ICP0 from herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):207–220. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90025-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Silverstein S. Herpes simplex viruses with mutations in the gene encoding ICP0 are defective in gene expression. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2916–2927. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2916-2927.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K. Cloning of the latency gene and the early protein 0 gene of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5260–5271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5260-5271.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., McCarthy A. M., Schaffer P. A. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 in the gene encoding immediate-early regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):558–570. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.558-570.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disney G. H., Everett R. D. A herpes simplex virus type 1 recombinant with both copies of the Vmw175 coding sequences replaced by the homologous varicella-zoster virus open reading frame. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2681–2689. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed mutational analysis of Vmw110, a trans-acting transcriptional activator encoded by herpes simplex virus type 1. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2069–2076. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Analysis of the functional domains of herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early polypeptide Vmw110. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90521-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felser J. M., Kinchington P. R., Inchauspe G., Straus S. E., Ostrove J. M. Cell lines containing varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 62 and expressing the "IE" 175 protein complement ICP4 mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2076–2082. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2076-2082.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felser J. M., Straus S. E., Ostrove J. M. Varicella-zoster virus complements herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):225–228. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.225-228.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S., Hanson I. M., Trowsdale J. A novel cysteine-rich sequence motif. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90229-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Identification of immediate early genes from herpes simplex virus that transactivate the virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5265–5269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Brunel P. A. Varicella-zoster virus: isolation and propagation in human melanoma cells at 36 and 32 degrees C. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):199–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.199-203.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of viral early and late genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):700–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Ostrove J. M. Differential regulation by varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus type-1 trans-activating genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):710–714. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. J., Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcriptional activation by the pseudorabies virus immediate early protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2376–2382. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. M., McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 deletion mutants exhibit altered patterns of transcription and are DNA deficient. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.18-27.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Characterization of a potent varicella-zoster virus-encoded trans-repressor. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5289–5296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5289-5296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry L. J., Rixon F. J., Everett R. D., Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J. Characterization of the IE110 gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2365–2380. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Knipe D. M. Gene-specific transactivation by herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3814–3823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3814-3823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Mendoza G. E. A herpesvirus regulatory protein appears to act post-transcriptionally by affecting mRNA processing. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):848–863. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Schaffer P. A. Mutants defective in herpes simplex virus type 2 ICP4: isolation and preliminary characterization. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1092–1097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1092-1097.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow E. C., Stow N. D. Complementation of a herpes simplex virus type 1 Vmw110 deletion mutant by human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1989 Mar;70(Pt 3):695–704. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-3-695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stow N. D., Stow E. C. Isolation and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant containing a deletion within the gene encoding the immediate early polypeptide Vmw110. J Gen Virol. 1986 Dec;67(Pt 12):2571–2585. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-12-2571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Wigdahl B. Identification of dominant-negative mutants of the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2261–2267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2261-2267.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth U. V., Fraefel C., Vogt B., Vlcek C., Paces V., Schwyzer M. Immediate-early RNA 2.9 and early RNA 2.6 of bovine herpesvirus 1 are 3' coterminal and encode a putative zinc finger transactivator protein. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2763–2772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2763-2772.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





