Abstract
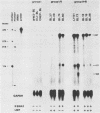
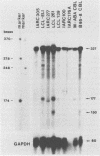
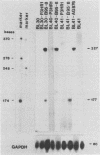
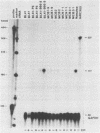
Transcription of the terminal protein (TP) gene of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in Burkitt's lymphoma cells, in EBV-negative Burkitt's lymphoma cells converted with transformation-defective (P3HR1) and transformation-competent (B95-8, AG876) EBV strains, and in EBV-immortalized cell lines was studied. A TP1 cDNA probe spanning the boundary between exons 1 and 2 and discriminating between TP1 and TP2 transcripts was used for S1 analysis. TP RNA expression varied widely in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. TP-specific transcripts were not detectable or only hardly detectable in Burkitt's lymphoma cells with the group I phenotype (CD10+ CD77+ CD21- CD23- CD30- CDw70-) as well as in P3HR1 virus-converted Burkitt's lymphoma lines. TP expression was high in Burkitt's lymphoma lines with the group II and group III phenotypes (CD21+ CD23+ CD30+ CDw70+), in B95-8 and AG876 virus-converted lines, and in EBV-immortalized cells. Detection of TP1 RNA correlated with EBNA2 expression. TP1 transcription was shown to be dependent on EBNA2 expression by stable transfection of an EBNA2 expression vector into P3HR1 virus-converted BL41 cells. EBNA2 is activating the TP1 as well as the TP2 promoter, as shown by the analysis of TP promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase constructs transiently transfected into EBNA2-positive and EBNA2-negative Burkitt's lymphoma cells.
Full text
PDF

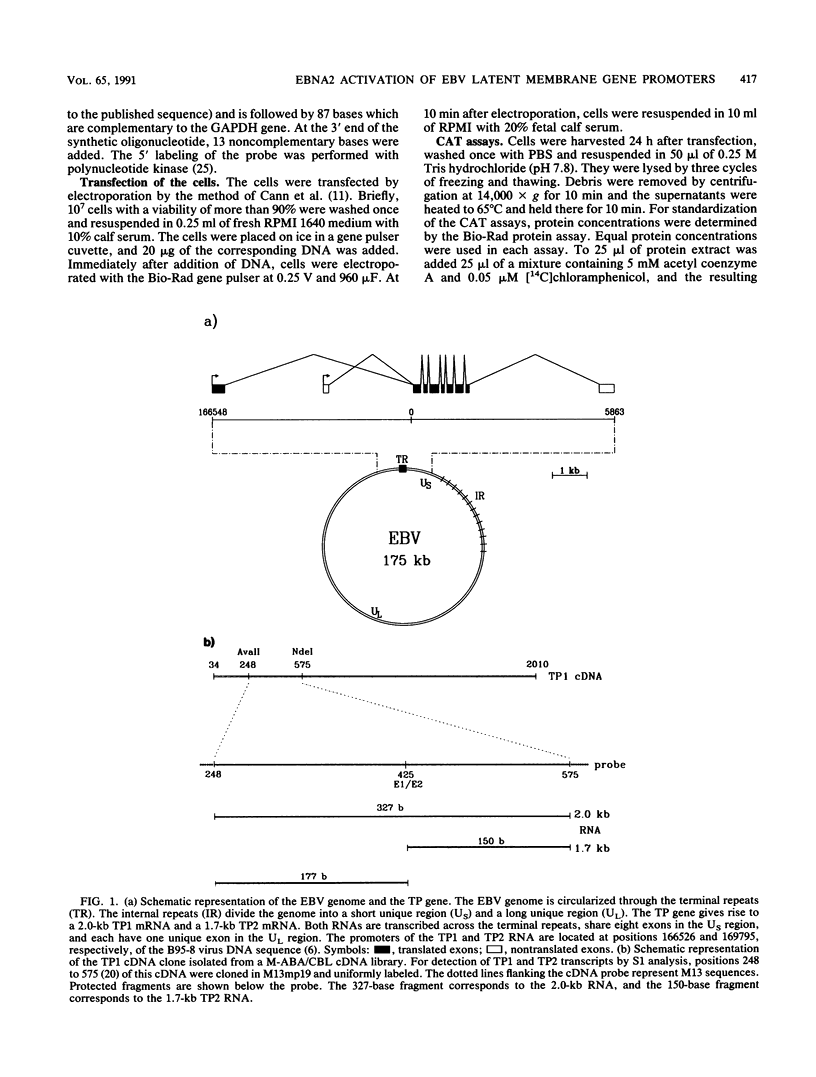
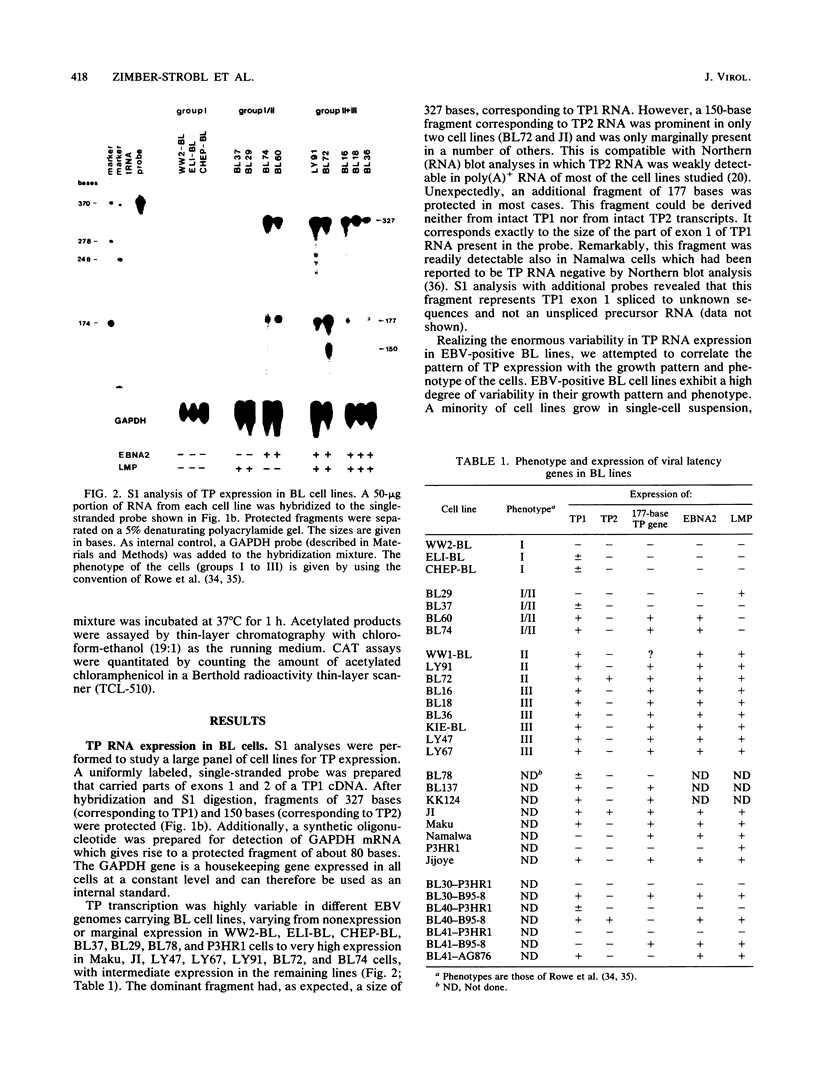
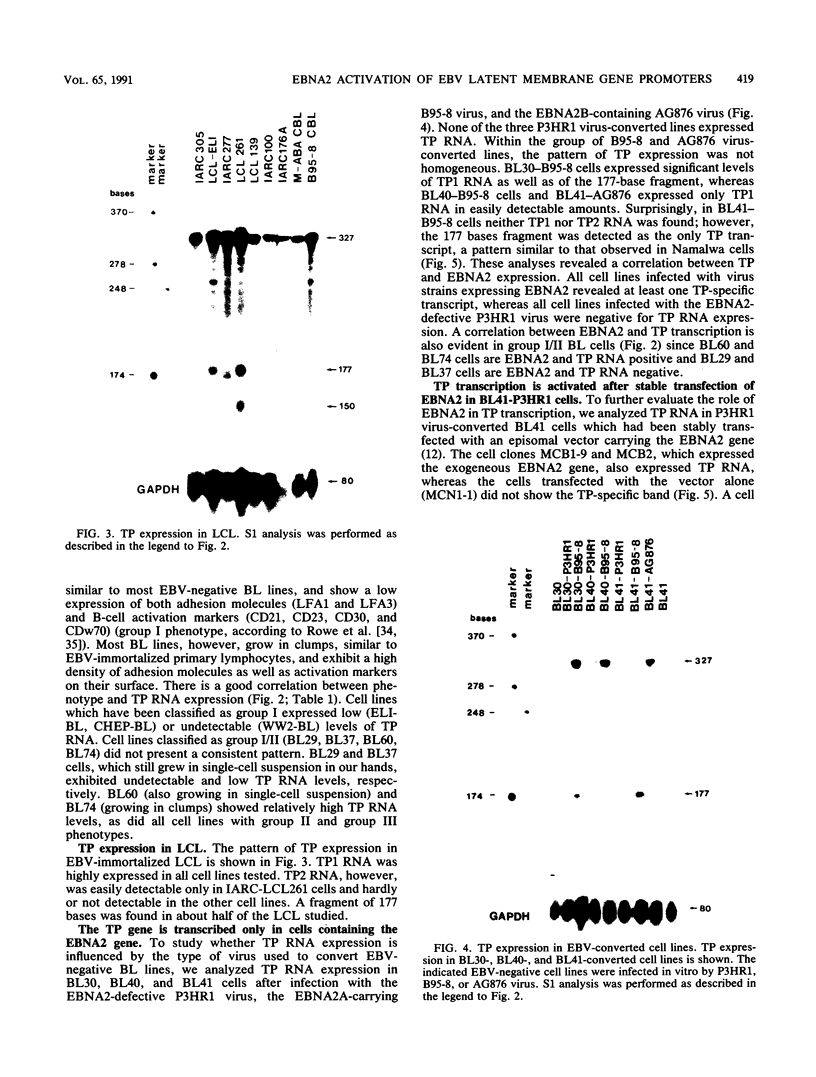
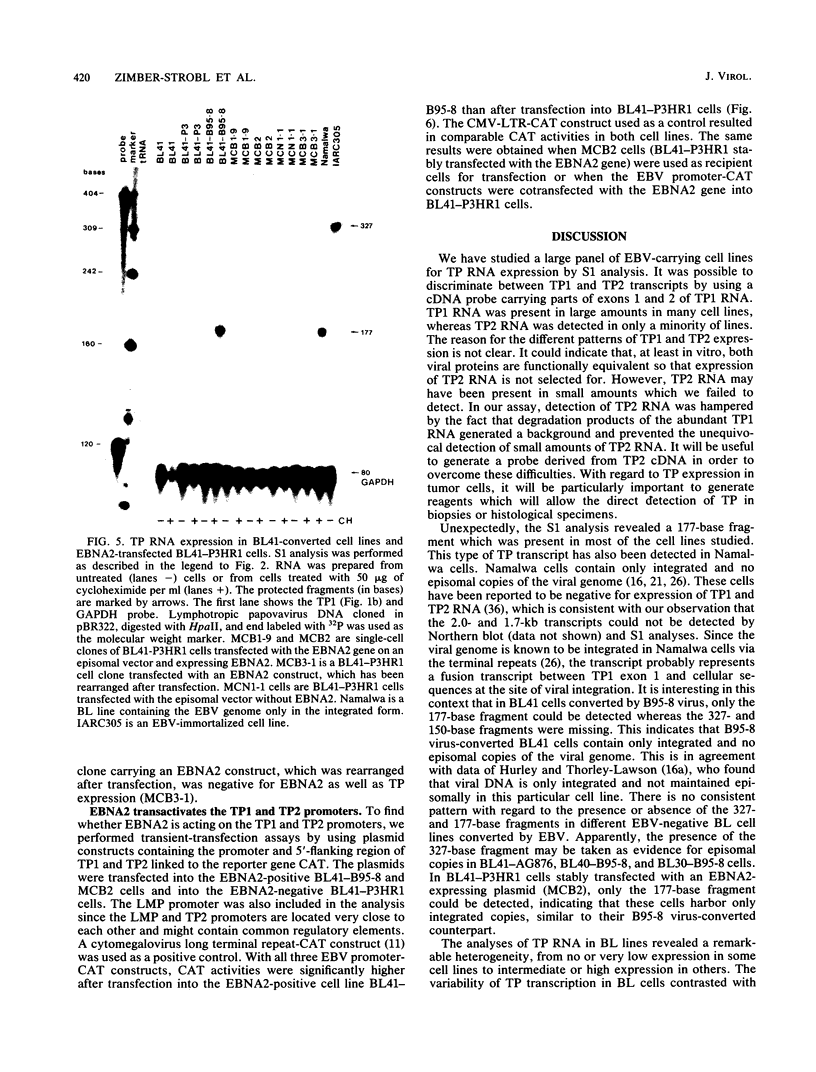


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbot S. D., Rowe M., Cadwallader K., Ricksten A., Gordon J., Wang F., Rymo L., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces expression of the virus-encoded latent membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2126-2134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Griffin B. E. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1755–1764. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen R. W., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Identification of the 37-kDa protein displaying a variable interaction with the erythroid cell membrane as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):649–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson-Anvret M., Lindahl T. Integrated viral DNA sequences in Epstein-Barr virus-converted human lymphoma lines. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):710–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.710-718.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. The multiple membrane-spanning segments of the BNLF-1 oncogene from Epstein-Barr virus are required for transformation. Oncogene. 1989 Jan;4(1):67–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornkamm G. W., Hudewentz J., Freese U. K., Zimber U. Deletion of the nontransforming Epstein-Barr virus strain P3HR-1 causes fusion of the large internal repeat to the DSL region. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):952–968. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.952-968.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Zimber U., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Banchereau J., Tursz T., Bornkamm G., Lenoir G. M. Stable transfection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 in lymphoma cells containing the EBV P3HR1 genome induces expression of B-cell activation molecules CD21 and CD23. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1002-1013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech B., Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Pavlish O., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus terminal protein 1 (TP1) in extracts of four lymphoid cell lines, expression in insect cells, and detection of antibodies in human sera. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2759–2767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2759-2767.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D., Kieff E. cis-acting regulatory elements near the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein transcriptional start site. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1855–1858. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1855-1858.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson A., Ripley S., Heller M., Kieff E. Chromosome site for Epstein-Barr virus DNA in a Burkitt tumor cell line and in lymphocytes growth-transformed in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1987–1991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeang K. T., Hayward S. D. Organization of the Epstein-Barr virus DNA molecule. III. Location of the P3HR-1 deletion junction and characterization of the NotI repeat units that form part of the template for an abundant 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate-induced mRNA transcript. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):135–148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.135-148.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Economou A., Farrell P. J. The terminal protein gene 2 of Epstein-Barr virus is transcribed from a bidirectional latent promoter region. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):3079–3084. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-3079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Villnave C. A., Singer R. H. Sensitive, high-resolution chromatin and chromosome mapping in situ: presence and orientation of two closely integrated copies of EBV in a lymphoma line. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):51–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90530-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir G. M., Vuillaume M., Bonnardel C. The use of lymphomatous and lymphoblastoid cell lines in the study of Burkitt's lymphoma. IARC Sci Publ. 1985;(60):309–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Adams A., Bjursell G., Bornkamm G. W., Kaschka-Dierich C., Jehn U. Covalently closed circular duplex DNA of Epstein-Barr virus in a human lymphoid cell line. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 15;102(3):511–530. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90331-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Kieff E. A second Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP2) is expressed in latent infection and colocalizes with LMP1. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2319–2326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2319-2326.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo T., Heller M., Petti L., O'Shiro E., Kieff E. Persistence of the entire Epstein-Barr virus genome integrated into human lymphocyte DNA. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1322–1325. doi: 10.1126/science.6095452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray R. J., Young L. S., Calender A., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Lenoir G. M., Rickinson A. B. Different patterns of Epstein-Barr virus gene expression and of cytotoxic T-cell recognition in B-cell lines infected with transforming (B95.8) or nontransforming (P3HR1) virus strains. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):894–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.894-901.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polack A., Hartl G., Zimber U., Freese U. K., Laux G., Takaki K., Hohn B., Gissmann L., Bornkamm G. W. A complete set of overlapping cosmid clones of M-ABA virus derived from nasopharyngeal carcinoma and its similarity to other Epstein-Barr virus isolates. Gene. 1984 Mar;27(3):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Finerty S., Edwards C., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Endemic Burkitt's lymphoma: phenotypic analysis of tumor biopsy cells and of derived tumor cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Sep;77(3):681–687. doi: 10.1093/jnci/77.3.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Hall L., Joab I., Laux G. Identification of the Epstein-Barr virus terminal protein gene products in latently infected lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2866–2875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2866-2875.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Rowe M., Evan G. I., Wallace L. E., Farrell P. J., Rickinson A. B. Restricted expression of EBV latent genes and T-lymphocyte-detected membrane antigen in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rooney C. M., Rickinson A. B., Lenoir G. M., Rupani H., Moss D. J., Stein H., Epstein M. A. Distinctions between endemic and sporadic forms of Epstein-Barr virus-positive Burkitt's lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1985 Apr 15;35(4):435–441. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.933-937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Larson R., Springer T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]