Fig. 6.
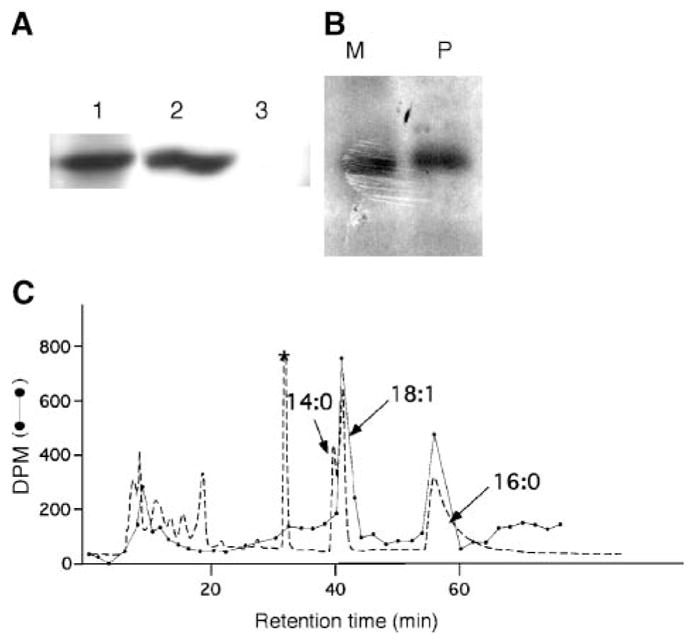
cPLA2γ is acylated with palmitic and oleic acids but it is not myristoylated. A: cPLA2γ was immunoprecipitated from cell homogenates of IMLF−/− cells infected with Ad-cPLA2γ using anti-cPLA2γ antiserum (lane 1) or preimmune serum (lane 3) and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-cPLA2γ antiserum. The Western blot of homogenate, before immunoprecipitation, is shown in lane 2. B: cPLA2γ was immunoprecipitated from [3H]palmitic (P) or [3H]myristic (M) acid-labeled IMLF−/−, separated by SDS-PAGE, and subjected to fluorography. C: HPLC analysis of fatty acid esters released from cPLA2γ. Fatty acids released from cPLA2γ by treatment with aqueous NaOH were converted to their pentafluorobenzyl esters. The dashed line represents the absorbance at 254 nm and reveals the position of the pentafluorobenzyl esters of the nonradiolabeled fatty acid standards added to the reaction mixture: myristic acid (14:0), oleic acid (18:1), and palmitic acid (16:0) (indicated by arrows). The absorbance peak marked with an asterisk is derived from esterification reagents, because it was seen in a blank run containing only reagents. The absorbance peaks eluting earlier than 20 min are attributable to unknown substances, presumably hydrophilic material derived from impurities present in the cPLA2γ sample. The dotted line indicates the amount of tritium (dpm) in each column fraction. The total dpm of tritium eluting from the column is 85% of that injected.
