Figure 6.
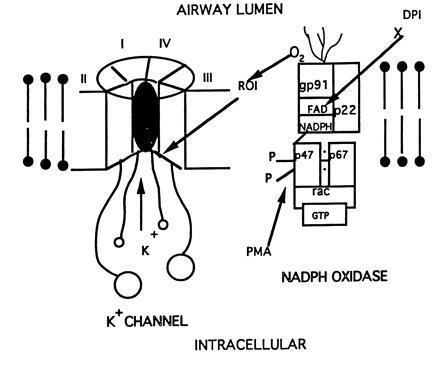
In this simplified model, the NADPH oxidase complex [modified from Segal and Nugent (35)] is shown to associate with the specific K+ channel protein. In one scenario, signaling of the ion channel response may be mediated via reactive oxygen intermediates (ROI) generated by the oxidase. Another scenario may involve signaling via metabolites at the cytoplasmic aspects of the complex (e.g., reductive events). We also indicate that DPI can inhibit oxidase function through inhibition of the flavoprotein activity while PMA can stimulate phosphorylation (i.e., activation) of the cytoplasmic components of the oxidase complex. Our immunohistochemical and electrophysiological data support functional cooperation between the oxidase and the K+ channel during O2 sensing.
