Figure 1.
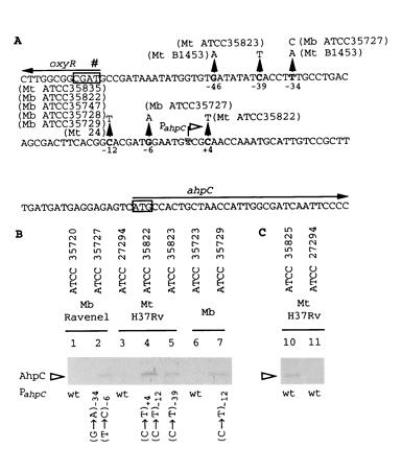
(A) DNA sequence of the oxyR–ahpC intergenic region from M. tuberculosis and M. bovis. The previously reported (17, 22) and additional mutations are indicated by upward pointing triangles. Positions of the nucleotide substitutions are relative to the ahpC mRNA start site (Fig. 2). Strain designations are given next to the corresponding mutations. Boxed sequences, start codon of ahpC and the destroyed start codon (#) of oxyR (17). Arrows, direction of transcription. (B) Western blot analysis of AhpC production in three series of INHr derivatives that carry ahpC promoter mutations in addition to katG lesions. Lanes: 2, 4, 5, 7, INHr derivatives; 1, 3, and 6, parental INHs strains. (C) AhpC production in an INHr derivative (lane 10) of M. tuberculosis H37Rv (lane 11) that does not carry the ahpC promoter alterations. Anti-DirA antibody that recognizes mycobacterial AhpC (18, 23) was used for Western blot analysis. The strains tested are indicated above the blot and the corresponding ahpC promoter mutations are indicated below the blot. Mb, M. bovis; Mt, M. tuberculosis; wt, wild type.
