Figure 3.
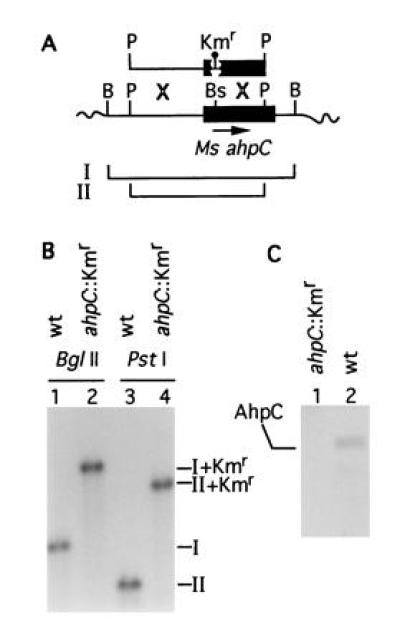
Inactivation of ahpC on the chromosome of M. smegmatis. (A) Schematic representation of the recombinational events between chromosomal ahpC and ahpC::Kmr on a 2.5-kb PstI fragment introduced into M. smegmatis mc2 155 by electroporation. B, BglII; P, PstI; Bs, BspEI. Balloon, 1.2-kb Kmr cassette. Lines I and II correspond to the wild-type BglII and PstI fragments, respectively. (B) Southern blot hybridization analysis of the insertional inactivation of ahpC in the strain VD1865-6. Lanes: 1 and 3, M. smegmatis mc2 155 ahpC+; 2 and 4, M. smegmatis VD1865-6. I, 1.7-kb BglII fragment (wt); II, 1.3-kb PstI fragment (wt). I+Kmr (2.9 kb) and II+Kmr (2.5 kb) are the corresponding bands hybridizing with the ahpC probe in the strain VD1865-6. (C) Western blot analysis of AhpC expression in the parent strain M. smegmatis mc2 155 (wt) and its mutant derivative VD1865-6 (ahpC::Kmr). Equal amounts of protein from crude extracts separated by SDS/PAGE were probed with anti-DirA antibody.
