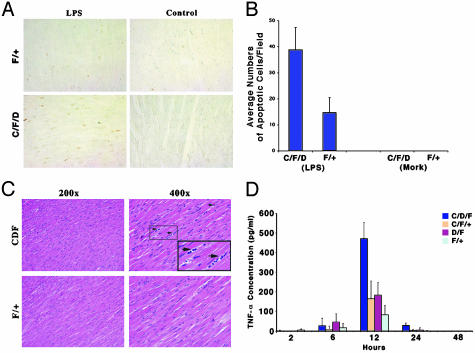
Fig. 3.
Endotoxin-induced cardiac apoptosis and possible inflammatory responses in knockout and control mice. (A) Cardiac tissue samples from representative animals after 39 h of LPS treatment were examined by terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining (dark brown nuclei are positive). F/+, WT; C/F/D, knockout mice. (B) Bar graph showing average (n = 8) numbers of TUNEL-positive staining cells. (C) Hematoxylin/eosin staining of heart sections obtained 39 h after LPS treatment. (Upper) Possible inflammatory cells (arrow) throughout heart sections with low (Left, ×200) and high (Right, ×400) magnification [knockout (C/F/D) or WT (F/+) animals]. Mononuclear infiltrating cells are indicated by arrows. (D) Secreted TNF-α levels in isolated cardiomyocyte cultures from neonatal mice with the indicated genotypes. Cultures were incubated with or without LPS for 2, 6, 12, and 24 h.