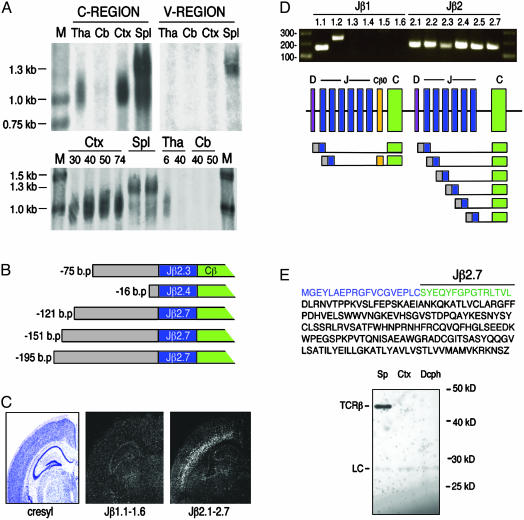
Fig. 3.
Neuronal TCRβ is transcribed from unrearranged genomic loci. (A Top) Northern blot analysis of RNA derived from P9 thalamus (Tha), P29 cerebellum (Cb), P30 cortex (Ctx), and adult spleen (Spl), probed with TCRβ C region or mix of V region probes. (Bottom) RNA derived from P30, P40, P50, and P74 cortex, adult spleen, P6 and P40 thalamus, and P40 and P50 cerebellum, probed for TCRβ C region. M, molecular weight markers. (B) RACE-derived sequences indicate that the 5′ ends of neuronal TCRβ are identical with genomic sequences 5′ to several of the TCRβ J regions. Numbers indicate bases from the beginning of transcript to Jβ exon junction. (C) In situ hybridization of adult mouse brain sections by using probes for genomic sequence spanning Jβ1.1–1.6 or Jβ2.1–2.7 indicates that the majority of neuronal TCRβ mRNA includes Jβ2 regions. (D) RT-PCR by using primers ≈20 bp 5′ to the start of each Jβ coding region indicated, plus a common C region 3′ primer, indicate that neuronal TCRβ transcripts include at least 8 of the 12 Jβ regions and include noncoding intergenic sequences upstream of Jβ regions. One sequence that included Jβ1.2 also included the Cβ0 exon. (E) Hypothetical truncated TCRβ protein sequence. (Top) Amino acid sequence of hypothetical protein encoded by genomic region 5′ to Jβ2.7 (blue), Jβ2.7 (green), and C region (black). (Bottom) Immunoprecipitation/Western blot analysis of saline-perfused brain tissue using an antibody to the C region of TCRβ. LC, light chain; Sp, spleen; Ctx, cortex; Dcph, diencephalon. Analyzed were 100 μg of spleen tissue and 5 mg of cortex and diencephalon.