Figure 4.
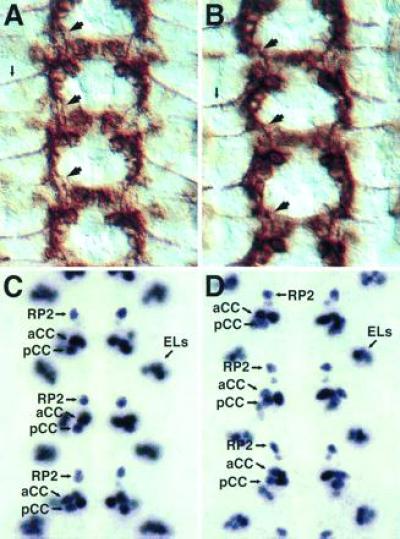
Early-extending axons and cell fates are normal in kuz mutants. Each panel shows three segments of the CNS. (A) A wild-type stage 13 embryo stained with mAb 1D4. Fas II is expressed on a subset of neurons, including the longitudinal connective pioneer neuron pCC and the aCC motoneuron. The pCC axon navigates anteriorly through the connective (large arrows). The aCC axon exits the CNS laterally (small arrow). (B) A kuz mutant stage 13 embryo stained with mAb 1D4. The normal pattern of cells express Fas II. The pCC axon extends its axon through the longitudinal connective (large arrows) and the aCC axon exits the CNS laterally (small arrow), as in wild-type embryos. Overall the CNS is very close to wild type at this stage. (C) A wild-type stage 15 embryo stained with mAb 3C10, which recognizes the Even-skipped nuclear protein. Even-skipped is expressed in a small subset of CNS cells, including the RP2 and aCC motoneurons and the pCC interneuron, as well as a lateral cluster of cells known as the ELs (25). (D) A kuz mutant stage 15 embryo stained with mAb 3C10. The Even-skipped-positive cells are present and in their correct locations, indicting that the cell fates of these neurons are not altered in the kuz mutant.
