Figure 1.
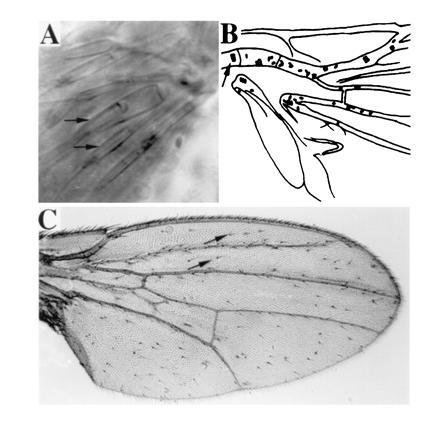
(A) In the scutellum of GAL4(109–68); UAS-ato fly, several scolopales, each formed as a part of an ectopic ch organ by its support cells (arrows mark two of the scolopales), are visible under Nomarski optics. (B) Camera lucida representation of the basal quarter region of the wing of an hs-GAL4; UAS-ato fly, examined directly with Nomarski optics. Each oval represents a ch organ. Wild-type ch organs on the ventral radius vein are indicated with an arrow; the rest of the ch organs are ectopic. (C) Numerous bristles are formed on the wing of an hs-GAL4; UAS-sc fly. Almost all the bristles, except for those on the wing margin, are ectopic ones (two of the ectopic bristles are marked with arrows).
