Fig. 5.
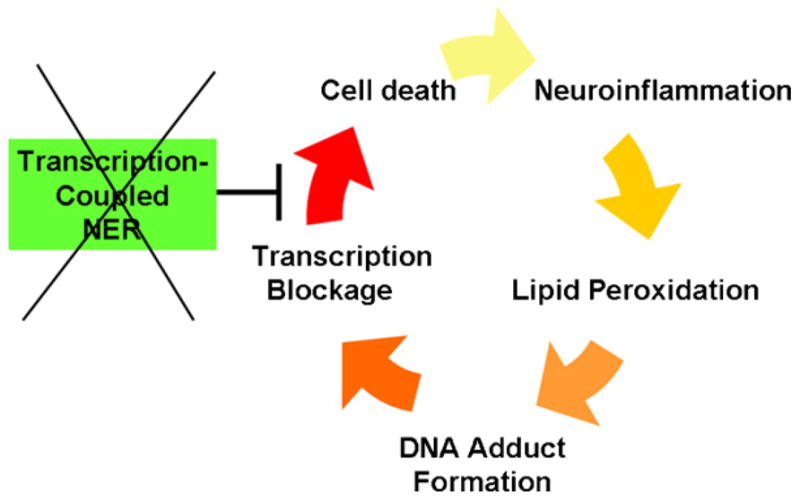
A speculative role for TC-NER in preventing a neuroinflammatory cycle of dysmyelination and calcification of the brain in CS. Inflammation results in lipid peroxidation and transcription-blocking DNA damage, which is repaired by TC-NER. CS gene mutations inactivate TC-NER, resulting in cell death, and in turn more inflammation from phagocytic cells. Under these conditions, the transcriptional defects in CS cells under conditions of DNA damage [78,79] may also play a role.
