Figure 1. Stem Cell Location in Different Epithelial Tissues.
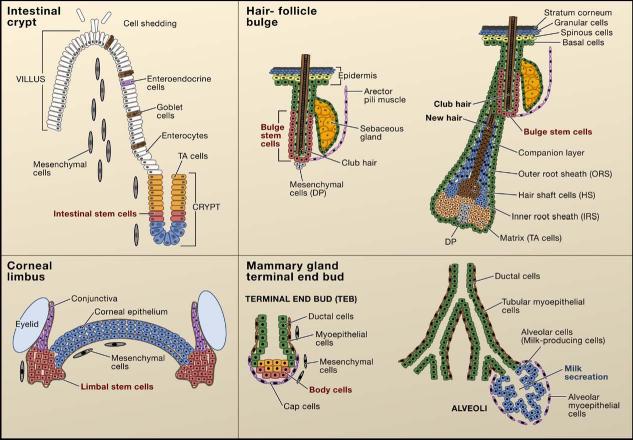
The intestinal crypt. The putative stem cells of the intestine (red) reside in a narrow band near the base of the crypt. These stem cells are thought to move downward to differentiate into Paneth cells (blue) or upward to generate proliferative transiently amplifying (TA) cells (orange). The intestinal TA cells differentiate upward into three lineages, enteroendocrine cells, goblet cells, and enterocytes, to form the villus. The corneal limbus. The cornea (blue) is a stratified epithelium that is flanked by the limbus (red) and the conjunctiva (purple). Corneal stem cells are thought to reside in the limbus region. The hair-follicle bulge. Label-retaining stem cells of the hair follicle reside below the sebaceous gland in a region known as the bulge, which is connected to the arector pili muscle. During periods of rest, bulge stem cells form the base of the follicle, which is adjacent to the specialized mesenchymal cells (dermal papillae). At the start of each hair cycle, stem cells at the bulge base become activated to form the highly proliferative new hair germ. As the germ grows, a proliferative compartment of TA cells (matrix cells) engulfs the dermal papilla at the base. These cells progress to differentiate to form seven concentric shells of discrete cell lineages, which are from outer to inner: the companion layer, the three layers of the inner root sheath, and the three layers of the hair shaft. These differentiated layers are surrounded by the outer root sheath, which extends below the bulge and is thought to contain stem cells that continue to migrate down to the follicle base during the growth phase of the hair cycle (Oshima et al., 2001). The interfollicular epidermis is a stratified epithelium with a basal layer that contains unipotent progenitor cells and TA cells. Basal cells differentiate upward to form the spinous, granular, and stratum corneum layers of the epidermis. The mammary gland terminal end bud. Stem cells of the mammary gland reside in the terminal end bud at the end of the mammary duct. The end of the terminal end bud is composed of body cells surrounded by cap cells. During pregnancy, the stem cells form a complex ductal structure containing ductal cells that end in the alveoli that produce milk components.