Figure 5.
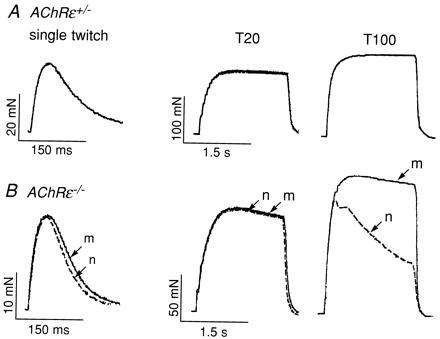
Reduction of isometric tetanic muscle contraction force. (A) Isometric tension measurements on soleus muscle in vitro from a heterozygous AChRɛ+/− animal at P32. Single twitches and tetanic contractions were evoked by direct muscle stimulation or by nerve stimulation in normal Tyrode solution. The records of contractions evoked by nerve or muscle stimulation superimposed perfectly indicating no difference in contraction force upon nerve or muscle stimulation. (B) Isometric tension measurements on soleus muscle from an AChRɛ−/− animal at P32. Single twitches and tetanic contractions evoked by direct muscle stimulation (m; solid lines) and nerve stimulation (n; dashed lines) are superimposed for direct comparison. Note different scales in A and B. Tetanic stimulation frequencies (T) were 20 or 100 Hz as indicated. Vertical scale bars indicate muscle contraction force in mN; horizontal ones indicate duration of stimulation in seconds (s). Body weight of the three animals studied in each group was on average 22 ± 4.1 g for the AChRɛ+/− mice and 11 ± 1.1 g for AChRɛ−/− mice; wet weight of soleus muscles was 11.5 mg ± 2.2 and 7.5 mg ± 1.1, respectively (n = 6 each) (P < 0.005 for each comparison, t test).
