Fig. 2.
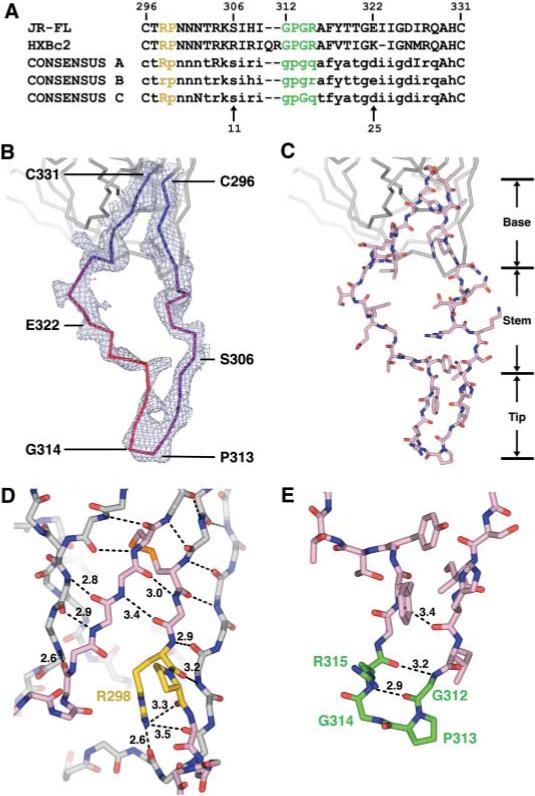
V3 sequence and structure. (A) V3 sequence. The sequences of JR-FL (17) and HXBc2 are shown along with the consensus sequence of clades A, B, and C. For the consensus sequences, absolutely conserved residues are shown in uppercase, with variable residues in lowercase (37). Single-letter aminoacid abbreviations: A, Ala; C, Cys; D, Asp; E, Glu; F, Phe; G, Gly; H, His; I, Ile; K, Lys; M, Met; N, Asn; P, Pro; Q, Gln; R, Arg; S, Ser; T, Thr; V, Val; Y, Tyr. The conserved (Arg-Pro) and (Gly-Pro-Gly-Arg) motifs are colored yellow and green, respectively, and are highlighted with the same colors in (D) and (E). (B) V3 electron density and B values. 2Fobs – Fcalc density is shown for the entire V3 region and contoured at 1σ. V3 is color-coded by B value from blue (lower atomic mobility) to red (higher mobility). (C) V3 structure. The entire V3 is shown (color code: salmon, carbon atoms; red, oxygen atoms; dark blue, nitrogen atoms; orange, disulfide bond). Regions corresponding to the fixed base, accordion-like stem, and β-hairpin tip are labeled. (D) Close-up view of the V3 base. From its N terminus (Cys296), V3 extends the antiparallel sheet on the outer domain of gp120. After hydrogen bonding for three residues, additional sheet contacts are interrupted by two conserved residues: Arg298, whose side-chain hydrogen bonds to three carbonyl oxygens, including two on the neighboring outer domain strand; and Pro299, which initiates the separation of outgoing and returning V3 strands. In the returning strand, antiparallel β-sheet interactions with core gp120 recommence with the carbonyl of residue 297 and continue to the disulfide at Cys331. Main-chain atoms are shown for the core and V3 base, colored the same as in (C). Hydrogen bonds are depicted with dashed lines, with select distances in Å. All atoms of the highly conserved Arg298, Pro299, and Cys296-Cys331 disulfide are shown, with Arg and Pro carbons highlighted in yellow and disulfide in orange. (E) Conformation of the V3 tip. From Ser306 to Gly312, the main chain assumes a standard β-conformation, which terminates in a Gly-Pro-Gly-Arg β-turn (residues 312 to 315) (29, 38). After the turn, the returning density is less well defined, indicative of some disorder. All atoms of the tip are colored as in (C), with carbon atoms of the conserved tip highlighted in green. Hydrogen bonds that stabilize the β hairpin are shown as in (D).
