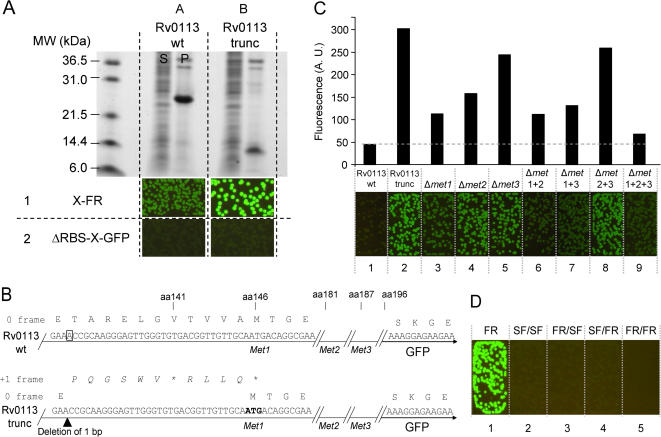
Figure 5. Characterization of a translation reinitiation artifact variant of Rv0113 isolated by directed evolution using C-terminal GFP FR.
(A) Directed evolution of insoluble wild-type Mtb protein Rv0113 (WT, row 1, column A) produced a truncated protein variant that appeared bright as a GFP fusion (EV, row 1, column B). The same variant subcloned into a GFP fusion vector without a vector-encoded ribosome initiation sequence (ΔRBS-GFP) failed to produce bright colonies (row2, column B). Soluble fraction (S), pellet fraction (P). (B) DNA sequence of wild type Rv0113 (top) and truncated Rv0113 (bottom) GFP fusions. A single base pair deletion in the original frame at codon 134 (boxed in wild type Rv0113 sequence) (top), (arrow head below Rv0113 trunc sequence), (bottom) resulted in a new stop codon at amino acid 141. The frame-shifted residues (italic script above the Rv0113 sequence) (bottom). First methionine codon in the frame with GFP following the artifact (bold script) (bottom). Amino-acid positions shown above the sequences (C) Images of E. coli colonies expressing N-terminal polyhistidine fusions with C-terminal fused GFP for wild-type Rv0113 (wt), evolved truncated variant (trunc), and the evolved truncated variant with directed methionine→leucine substitutions at methionine 146 (Δmet1), methionine 181 (Δmet2), and methionine 187 (Δmet3). Double and triple methionine→leucine substitutions are also shown (Δmet1 1+1, Δmet 1+3, Δmet 2+3, Δmet 1+2+3). Exposure time is 2 s. Bar graph (top) of liquid culture fluorescence after expression of the same constructs in shake cultures at 37°C. Fluorescence values were normalized by dividing by optical density at 600 nm. (D) Fluorescence of E. coli colonies expressing Rv0113 truncated variant with original C-terminal GFP and indicated GFPi 9/8 reporters. The colonies expressing the C-terminal fusions (FR) are brightly fluorescent (left image). Colonies expressing the corresponding GFPi fusion constructs (last four images). Exposure time is 2 s.