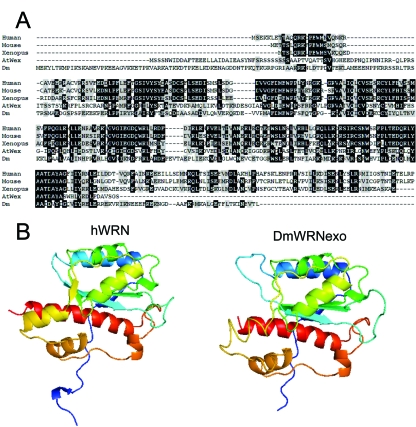
Fig. 1.
Homology of DmWRNexo to human WRN. (A) Alignment of WRN protein sequences from human, mouse, Xenopus laevis and Arabidopsis thaliana (AtWEX) with full-length DmWRNexo (predicted from both our cloned CG7670 cDNA and genomic sequence (Flybase)). Black depicts residues identical in three or more species, with grey showing similarity. Note the highly conserved blocks of sequence flanking the catalytic core residues. D82 and E84 metal-ion co-coordinating residues (residues numbered for the human WRN protein) are marked with an asterisk. (B) SWISS-MODEL was used to predict the possible tertiary structure of DmWRNexo from residues 118–312, according to the known structure of human WRN exonuclease (2fbyA, Perry et al., 2006). Left panel shows the human WRN exonuclease domain while the right panel shows the predicted structure of Drosophila melanogaster DmWRNexo.