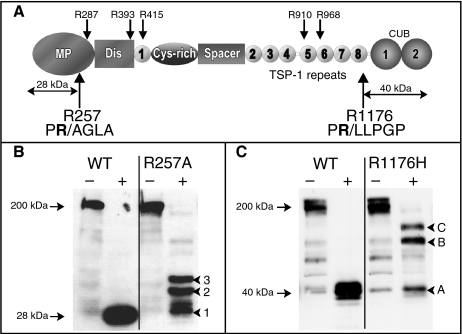
Fig. 1.
Identification of thrombin cleavage sites in ADAMTS-13. (A) Diagram of ADAMTS-13 domain structure. Locations of predicted thrombin cleavage sites after R287, R393, R415, R910 and R968 are shown above. Thrombin cleavage sites determined by N-terminal sequencing of cleavage fragments are shown below with the amino acid sequence of the amino acids that flank these sites. Single-letter amino acid code is shown, P1 arginine is highlighted in bold, cleavage site is denoted by (/). The location of the 28 and 40 kDa fragments detected in (B) and (C) are highlighted. (B) Wild-type (WT) ADAMTS-13 and ADAMTS-13(R257A) mutant were incubated with and without (+ and –) 10 nm thrombin for 6 h and analyzed by Western blotting using an antimetalloprotease domain monoclonal antibody (mAb). Proteolysis after R257 was prevented by substitution of the P1 arginine to alanine, and resulted in detection of alternative cleavage fragments 1, 2 and 3. (C) WT ADAMTS-13 and ADAMTS-13(R1176H) mutant were incubated with and without (+ and –) thrombin as in (B), and analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-CUB mAb. Proteolysis after R1176 was significantly inhibited by substitution of the P1 arginine to histidine resulting in detection of cleavage fragments A, B and C.