Figure 2. Syk inhibition suppresses the phagocytosis of Francisella.
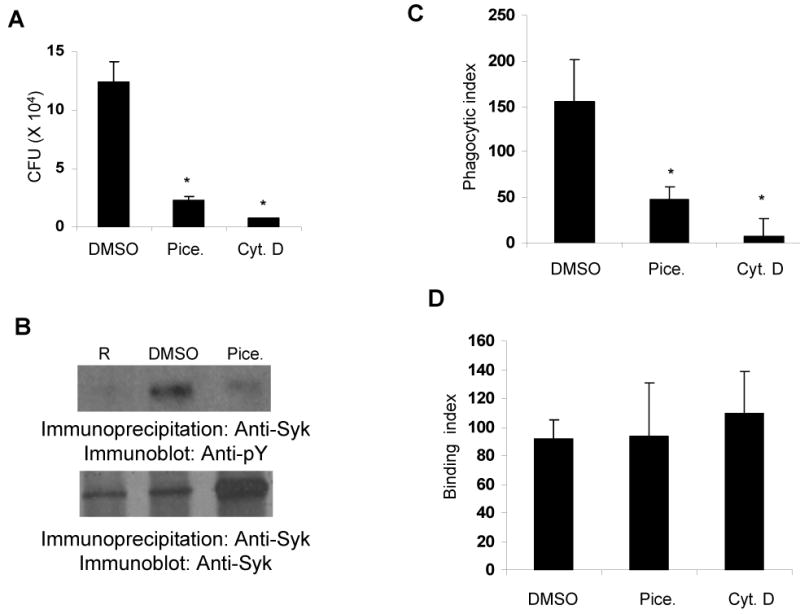
A. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with vehicle control (0.1% DMSO) or 25 μg/mL piceatannol (Pice.) or 5 μg/mL of cytochalasin-D (Cyt. D) for 30 minutes; cells were infected with 100 MOI of F. novicida for 1 hour and phagocytosis was assessed by CFU assays. B. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with vehicle control (0.1% DMSO) or 25 μg/mL piceatannol (Pice.) for 30 minutes; cells were infected with 100 MOI of F. novicida for 1 minute and phosphorylation of Syk was examined as described in the legend of Figure 1. C&D. RAW 264.7 cells were treated with 0.1 % DMSO or 25 μg/mL piceatannol (Pice.) or 5 μg/mL cytochalasin-D (Cyt. D) for 30 minutes, cells were infected with 100 MOI of F. novicida for 1 hour, phagocytosis (C) and binding (D) of the bacteria was analyzed by immunofluorescence. Phagocytic and binding indices are defined as the number of bacteria phagocytosed or adherent to 100 macrophages, respectively. Data represent mean and standard deviation of 3 independent experiments. *, p<0.05 compared to DMSO value.
