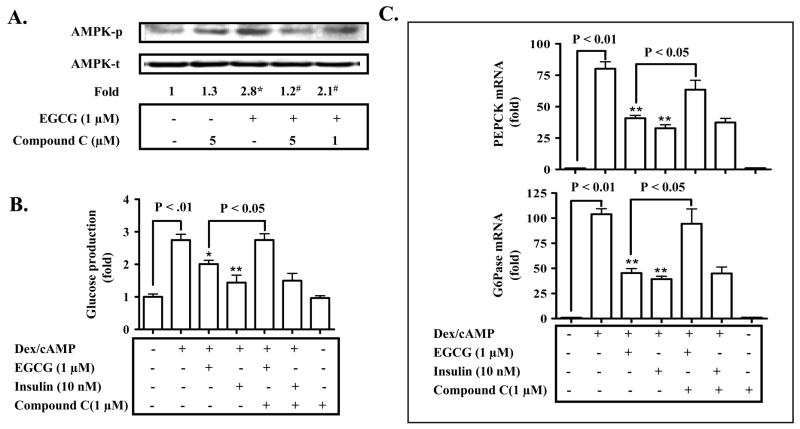
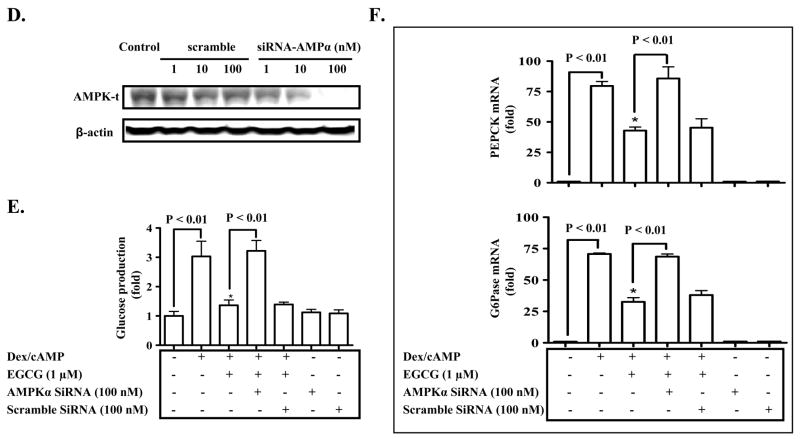
Fig. 4. AMPK mediates the EGCG repression of hepatic gluconeogenesis.
(A) Primary hepatocytes were pre-treated with Compound C for 30 min as noted, and then treated with EGCG for 10 min. Levels of phospho-/total AMPK were measured by immunoblotting, and quantified by densitometry. Levels of phospho-AMPK were normalized to total AMPK. *: p < 0.05 compared to untreated cells; #: p < 0.05 compared to EGCG treatment. (B) Cells were sequentially treated with Compound C for 30 min, EGCG or insulin for 3 h in the serum-free Williams’ E medium, and then washed with the pre-warmed glucose-free DMEM medium 3 times. Subsequently, cells were stimulated by cAMP/dexamethasome in the presence of EGCG or insulin for 3 h in glucose-free DMEM medium. Gluconeogenic substrates were added to some cells. The glucose production via gluconeogenesis was quantified and calculated as detailed in “Materials and Methods). *: p<0.05 and **: p<0.01 compared to Dex/cAMP treatment. (C) Transcripts of PEPCK and G6Pase genes in cells similarly treated as described in (B) were quantified by the Taqman Real-time PCR and normalized to GADPH. *: p<0.05 compared to Dex/cAMP + insulin. (D) Hepatocytes were transfected with siRNA duplexes as noted. Levels of the AMPK protein were detected by immunoblotting 26 h after the transfection. (E) and (F) Cells were transfected with siRNA duplexes for 26 h as noted prior to the treatment with EGCG or insulin. Stimulation of cells with cAMP/Dex and quantification of the glucose production via gluconeogenesis were performed as described above. Transcripts of PEPCK and G6Pase genes were quantified by the Taqman Real-time PCR and normalized to GADPH. *: P < 0.05 vs. cells treated with Dex/cAMP.