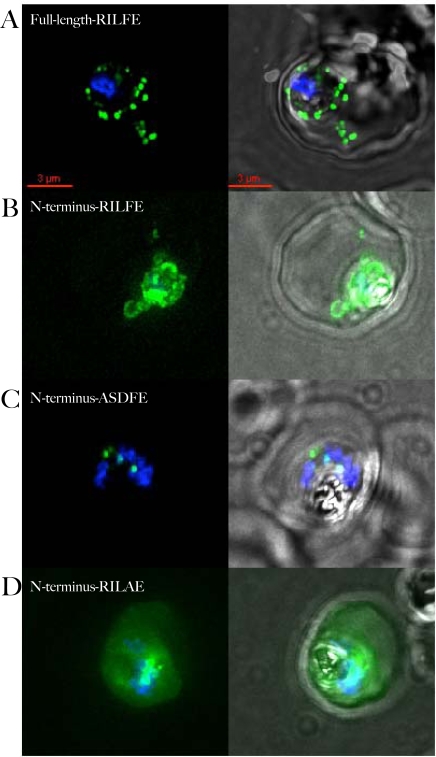
Figure 2. Export of PF14_0607-GFP requires full-length protein.
A) Localization of full-length PF14_0607 fused to GFP. The fusion protein is clearly detected in the erythrocyte cytosol. B) Fusion of the wild type N-terminal 89 amino acids to GFP is retained within the PV. Presence of GFP in cytoplasmic loops in the absence of staining in the erythrocyte cytoplasm indicates that the protein is secreted to the PV but not exported into the erythrocyte. C) Replacement of the HT-motif with unrelated sequence leads to retention of the protein inside the parasite. The punctate staining of the mutant fusion protein is reminiscent of apicoplast localization. D) Replacement of phenylalanine at position 4 in the HT-motif with an alanine residue allows the fusion protein to be exported. For each construct, the sequence of the HT-motif, or the sequence replacing it, is shown in the upper left hand corner of the panel. The overlap of GFP and Hoechst staining is shown in the left-hand panels, overlap with the phase contrast image is shown in the right-hand panels. All images are composites of multiple consecutive optical sections.