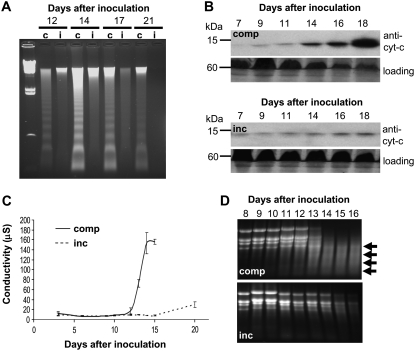
Figure 2.
Apoptosis-like PCD markers are associated with symptom expression during compatible but not incompatible interactions. A, Analysis of the integrity of host genomic DNA during symptom development of compatible (c) and incompatible (i) interactions. A clear and prolonged DNA laddering response is only observed during symptom development in the compatible interaction (Avalon versus isolate IPO323). B, Western-blot analysis of cytochrome c in the cytoplasmic fraction of compatible (top panels; comp) and incompatible (bottom panels; inc) leaves after fungal inoculation. The relative protein loading is displayed in each case for the 60-kD region. C, A loss of host cell membrane integrity during symptom development is restricted to the compatible interaction. Electrolyte leakage assays were performed on leaves undergoing incompatible (inc) or compatible (comp) interactions with the fungus on various days after inoculation. Note that despite visible symptoms appearing at the same time point, a rapid and dramatic loss of host membrane integrity is restricted to the compatible interaction. D, Large-scale degradation of host total RNA is associated with symptom development during the compatible (comp) interaction. Total RNA was isolated on the indicated days after inoculation and analyzed on agarose gels. Arrows indicate the appearance of degraded RNA species during symptom expression in the compatible interaction.