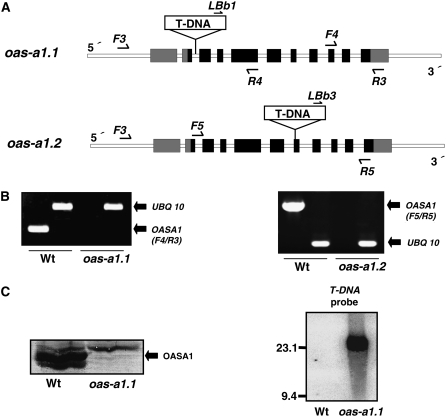
Figure 1.
Molecular characterization of the Arabidopsis oas-a1.1 and oas-a1.2 mutants. A, Intron-exon organization of the OAS-A1 gene (At4g14880) in the oas-a1.1 and oas-a1.2 T-DNA tagged mutants. LBb1, LBb3, F3, F4, F5, R3, R4, and R5 show the locations and directions of primers used in the screening for mutant plants. The OAS-A1 gene contains 11 exons (black squares with the untranslated regions shown in gray) and 10 introns (white squares). The gene structure and T-DNA region are not drawn to scale. B, RT-PCR analysis of the mutant plants. For RT-PCR, mRNA was prepared from the leaves of 2-week-old plants, and primers specific for OAS-A1 (F4/R3 in oas-a1.1 and F5/R5 in oas-a1.2) and UBQ10 transcripts were used. C, Western-blot (left) and Southern-blot (right) analyses of the oas-a1.1 mutant plant. For western blots, 15 μg of total protein from the leaves was electrophoresed and the OASTL isoforms were detected using antibodies raised against OAS-A1. For Southern blots, genomic DNA was digested with SpeI and hybridized with a T-DNA probe.