Fig. 2.
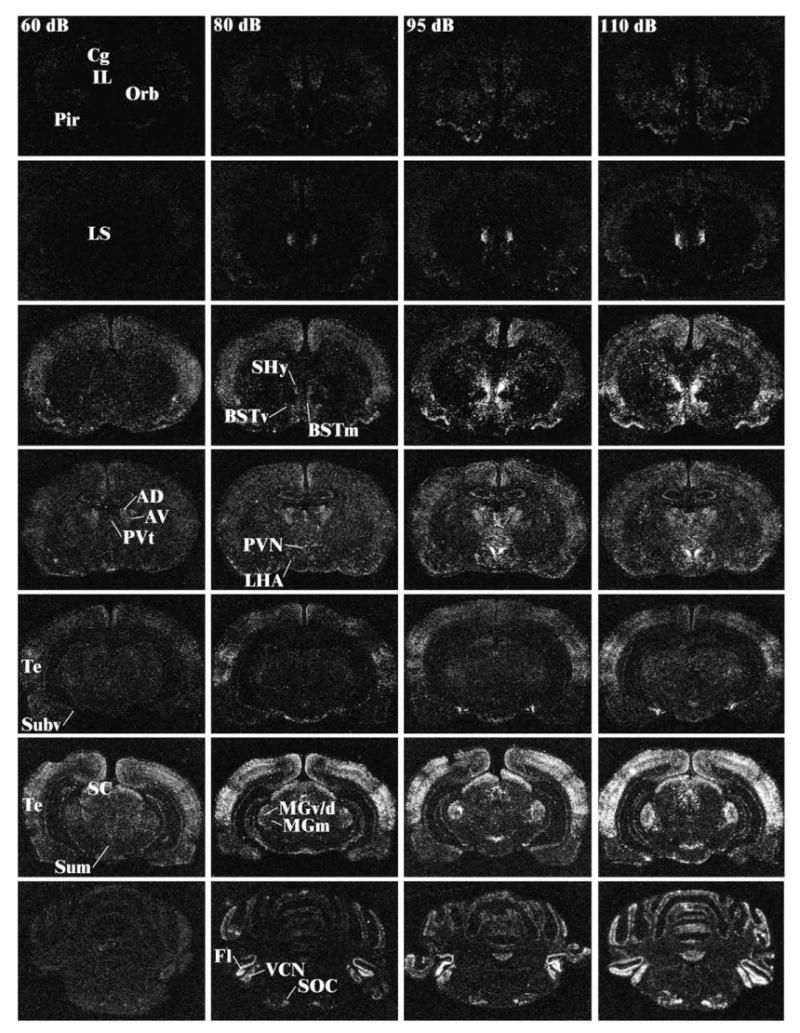
Representative photomicrographs of c-fos mRNA induction at different levels of the neuraxis for rats in the background noise condition (60 dB—far left column), 80 dB noise (middle left column), 95 dB (middle right column), and 110 dB (far right column). The different levels from top to bottom represent anterior to posterior brain sections. Note the increase in c-fos mRNA levels with increasing noise intensities in several brain regions. Abbreviations: AD, anterodorsal thalamic nucleus; AV, anteroventral thalamic nucleus; CG, cingulate cortex; BSTm, anteromedial bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; BSTv, anteroventral bed nucleus of the stria terminalis; IL, infralimbic cortex; Fl, flocculus; MGm, medial division of the medial geniculate body; MGv/d, ventral/dorsal divisions of the medial geniculate body; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; LS, lateral septum; Orb, orbitofrontal cortex; Pir, piriform cortex; PVN, paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus; PVt, anterior paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus; SC, superior colliculus; SHy, septohypothalamic nucleus; SOC, superior olivary complex; Subv, anteroventral subiculum; Sum, supramammillary nucleus of the hypothalamus; Te, temporal (auditory) cortex; VCN, ventral cochlear nucleus.
