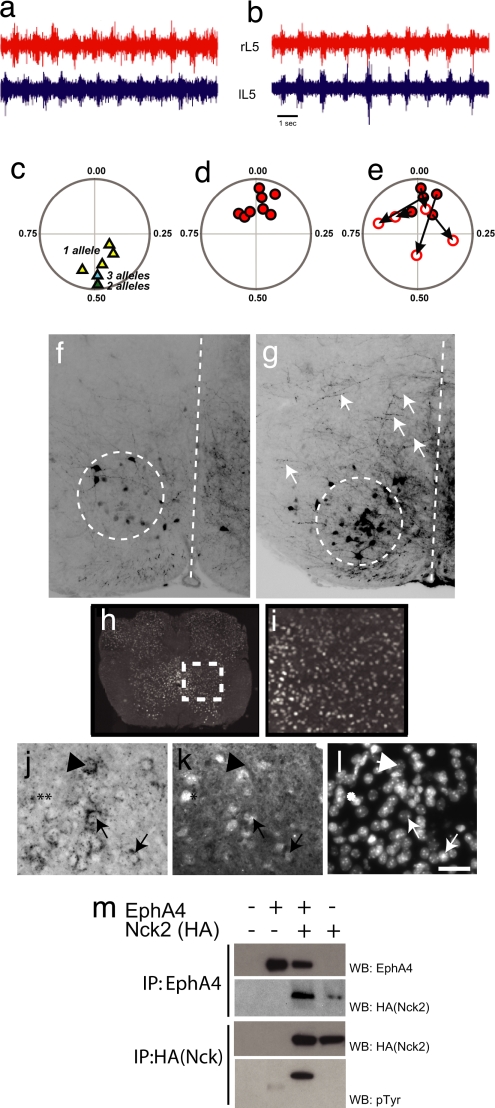
Fig. 3.
Loss of Nck leads to synchronous firing in bilateral ventral roots and defects in commissural axon guidance. (a and b) Representative trace recordings from the left (lL5) and right (rL5) ventral roots at the L5 level after the addition of NMDA and serotonin to isolated spinal cords from P2 control (Nck1+/−;Nck2flx/flx;Nestin-Cre) (a) and an Nck-deficient (Nck1−/−;Nck2flx/flx;Nestin-Cre) (b) mouse. (c and d) Circular-phase diagrams from control [Nck1+/−;Nck2flx/flx;Nestin-Cre (yellow triangles; n = 5); Nck1−/−;Nck2flx/flx (green triangle; n = 1); or Nck1+/−;Nck2flx/flx (blue triangle; n = 1)] (c) and Nck-deficient [Nck1−/−;Nck2flx/flx;Nestin-Cre (red circles; n = 8)] (d) mice. (e) Circular-phase diagram of Nck-deficient mice after the addition of 100 μM sarcosine. Filled red circles represent averaged vector plots of individual animals before sarcosine treatment. Open circles identify the final vector plot of individual animals after 20 min of sarcosine treatment. The arrows mark the movement of an individual animal's vector profiles after treatment. All recordings shown are from the L5 level. (f and g) Epifluorescent images of coronal sections through the L2 spinal cord after contralateral caudal application of rhodamine dextran amine (molecular weight, 3,000) crystals at the L4 level in control Nck1−/−;Nck2flx/flx (f) and Nck-deficient (g) mice. Descending CINs are found within the dashed circles. Dashed lines mark the midline. Arrows in g indicate fibers crossing the midline in Nck-deficient animals. (h and i) Nck1-β-gal expression of coronal sections through the lumbar spinal cord of an adult mouse. (i) Enlargement of boxed region shown in h. (j and k) EphA4-positive cells in the medial–ventrolateral spinal cord (j, arrows) that are Nck1-positive (k, arrows) as revealed by EphA4 RNA in situ hybridization (j) and β-gal antibodies (k). (l) Hoechst staining to show nuclei. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) Not all Nck1-positive cells are EphA4-positive, (j and k, asterisks), nor are all EphA4- positive cells Nck1-positive (j and k, arrowheads). (m) HEK293T cells were transfected as indicated. Lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with antibodies as indicated and probed with anti-EphA4 (top row), anti-HA antibodies (middle two rows), or anti-pTyr antibodies (bottom row).