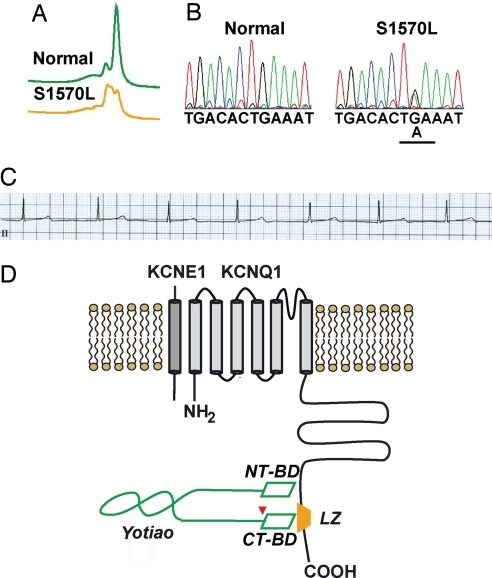
Fig. 2.
A missense variant, S1570L, in AKAP9-encoded Yotiao in human LQTS. (A) DHPLC analysis of the DNAs from the patient positive for S1570L-Yotiao and normal controls. (B) Chromatograms of DNA sequences of the patient positive for S1570L-Yotiao and normal control. Underlined G-to-A change in nucleotide sequence causes the S1570L (serine, S, to leucine, L) missense mutation in Yotiao. (C) ECG of S1570L-Yotiao-positive patient with symptomatic LQTS (QTc, 485 ms). (D) A schematic diagram of the IKs/Yotiao complex. Shown in gray color in the plasma membrane are KCNQ1 and KCNE1, α- and β-subunits of IKs, respectively. A leucine zipper motif (LZ) is located at the C terminus of KCNQ1 and is the binding site for Yotiao. AKAP Yotiao is depicted in green. NT-BD and CT-BD indicate the two KCNQ1-binding sites on Yotiao N and C termini. The LQTS-associated mutation S1570L is located close to the CT-BD, indicated by an arrow.