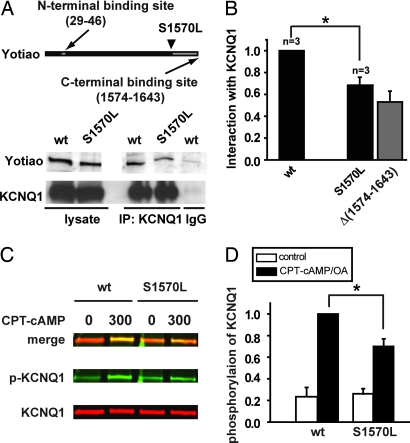
Fig. 3.
S1570L Yotiao reduces the interaction with and the cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of KCNQ1. (A) An anti-KCNQ1 antibody was used to precipitate the KCNQ1/Yotiao complex from the lysates of the transfected CHO cells. A control experiment was performed by using nonspecific goat IgG. Western blots (IB) of the lysates are shown (Left). Western blots of the immunocomplex are shown (Right). (B) The interactions between KCNQ1 and either WT- or S1570L-Yotiao are quantified by measuring Western blots of the immunocomplex after correcting the IP input errors. Results are normalized to WT-Yotiao. The S1570L mutation significantly reduced the interaction between KCNQ1. *, P < 0.05 (paired t test). Yotiao and KCNQ1. *, P < 0.05 (paired t test). The gray bar represents the interaction between KCNQ1 and Yotiao Δ(1,574–1,643) reproduced from Fig. 1 and is for comparison purposes only. (C) Phosphorylation of KCNQ1 was assayed in the cells expressing KCNQ1 with either WT- or S1570L-Yotiao. Lysates were analyzed by dual Western blot by using an infrared imaging system. Green signals (Middle) detect phosphorylated KCNQ1 (p-KCNQ1) protein. Red signals (Bottom) detect total KCNQ1 protein. A merged view is presented (Top). (D) S27 phosphorylated KCNQ1 is quantified by measuring the relative band intensity on the phospho-KCNQ1 Western blots after correcting for total KCNQ1 loading. *, P < 0.01.