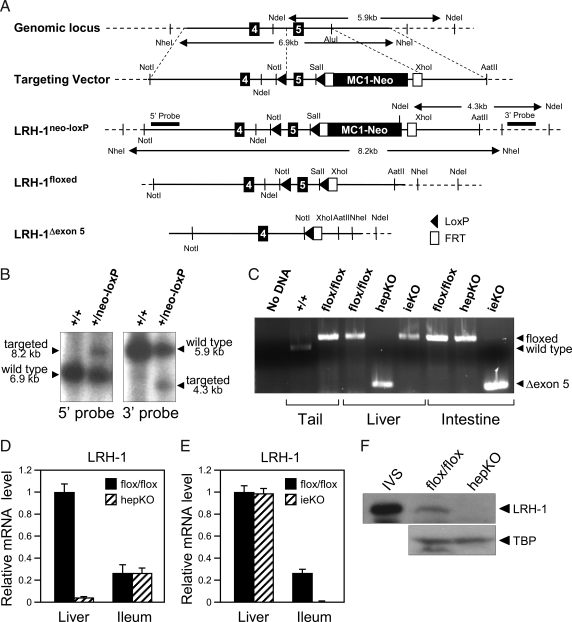
Figure 1.
Generation of Mice Deficient for LRH-1 in Liver or Intestine
A, Schematic representation of the targeting strategy to disrupt Lrh-1. The schematic shows exons 4 and 5 of Lrh-1, the targeting vector, and the targeted Lrh-1 allele both before and after successive removal of the MC1-neocassette with FLPe recombinase and exon 5 with cre recombinase. LoxP sites (solid arrowheads), FLPe recombinase target sites (Frt; open boxes), selected restriction enzyme sites and the 5′- and 3′-probes used for Southern blots are indicated. B, Southern blot analysis of DNA derived from wild-type (+/+) or targeted (+/neo-loxP) ES cells digested with NdeI or NheI and probed with 5′- and 3′-probes. Positions of wild-type and targeted alleles and their sizes are shown. C, PCR analysis of Lrh-1 alleles using DNA prepared from tail, liver, and intestine of Lrh-1+/+, Lrh-1flox/flox, hepKO, or ieKO mice as indicated. A control PCR reaction performed with no DNA is shown on the left. The positions of the PCR products generated by the wild-type Lrh-1 allele and the Lrh-1flox/flox (floxed) and deleted exon 5 Lrh-1 (Δexon 5) alleles are indicated by arrows on the left. D and E, RT-qPCR analysis done using a primer set that recognizes Lrh-1 exon 5 and cDNA from liver and ileum of either Lrh-1flox/flox and hepKO mice (D) or Lrh-1flox/flox and ieKO mice (E). F, Western blot analysis using in vitro synthesized LRH-1 (IVS) or nuclear extracts prepared from livers of Lrh-1flox/flox and hepKO mice and antibodies against LRH-1 or TATA-binding protein (TBP). The LRH-1 band migrates at approximately 62 kDa.