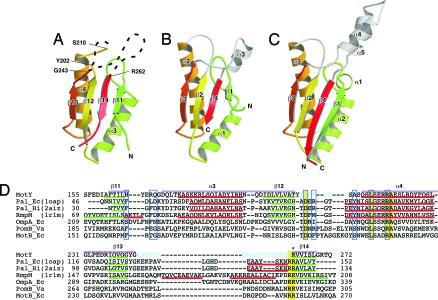
Fig. 2.
Comparison of OmpA/MotB-like domains. Cα ribbon representation of OmpA/MotB-like domain structures. (A) The C-terminal domain of MotY (MotY-C). (B) Pal of E. coli (1OAP). (C) The C-terminal domain of RmpM from N. meningitidis (1R1M). (D) Structure-based sequence alignment of the OmpA/MotB-like domains. The aligned sequences are: MotY, the C-terminal domain of V. alginolyticus MotY; Pal_Ec, E. coli Pal; Pal_Hi, H. influenzae Pal; RmpM, N. meningitidis RmpM; OmpA_Ec, E. coli OmpA; PomB_Va, V. alginolyticus PomB; and MotB_Ec, E. coli MotB. Residues highlighted in yellow are conserved in all seven proteins. Regions of secondary structure of MotY, Pal_Ec, Pal_Hi, and RmpM are indicated below the corresponding sequences as follows: Red line, α-helix; green line, β-strand. The secondary structure elements for MotY are labeled above the sequence. The residues contributing to the binding of the peptidoglycan precursor in Pal_Hi are indicated by blue boxes. The Arg-262 residue of MotY, which is important for motility and is conserved in OmpA/MotB-like proteins, is marked with an asterisk. Disordered residues in the MotY crystal structure are shown in cyan. The pink bars above the sequences represent the regions used to align the structures.