Figure 1.
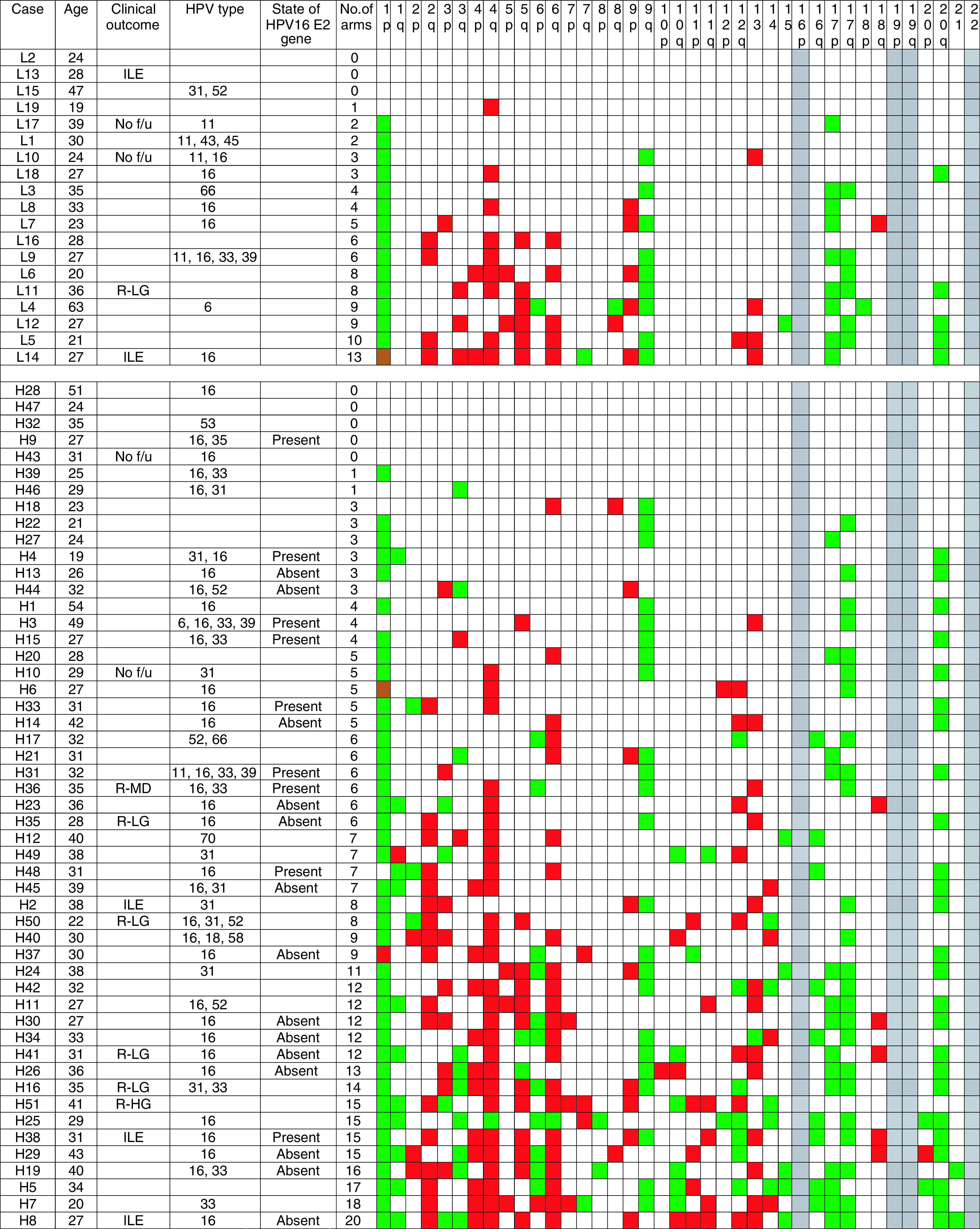
Clinicopathological data and frequency of CNIs in the 70 SILs studied. Prefix L denotes low-grade SIL and prefix H denotes high-grade SIL. Clinical outcome is shown if noteworthy. (ILE=inadequate local excision; No f/u=no follow-up data available; R-LG=recurred with a histological diagnosis of LG-SIL; R-HG=recurred with a histological diagnosis of HG-SIL; R-MiD=recurred with cytological mild dyskaryosis). Also listed are patient age; HPV types detected in the 53 cases analysed; the presence or absence of the HPV16 E2 gene in cases of HG-SIL that were HPV16 positive and tested (n=23); and the number of chromosome arms showing DNA CNI. Cases are sorted by a grade of SIL and then ranked by the number of arms showing CNI. For each arm, white boxes indicate no CNI, green boxes indicate gain, red boxes indicate loss and green/red striped boxes indicate gain and loss on the same arm. No data are shown for chromosomes 16p, 19 and 22, for which analysis by CGH is unreliable. In all 23 cases of HG-SIL tested for the state of the HPV16 E2 gene, the HPV16 E7 gene was detectable.
