Figure 5.
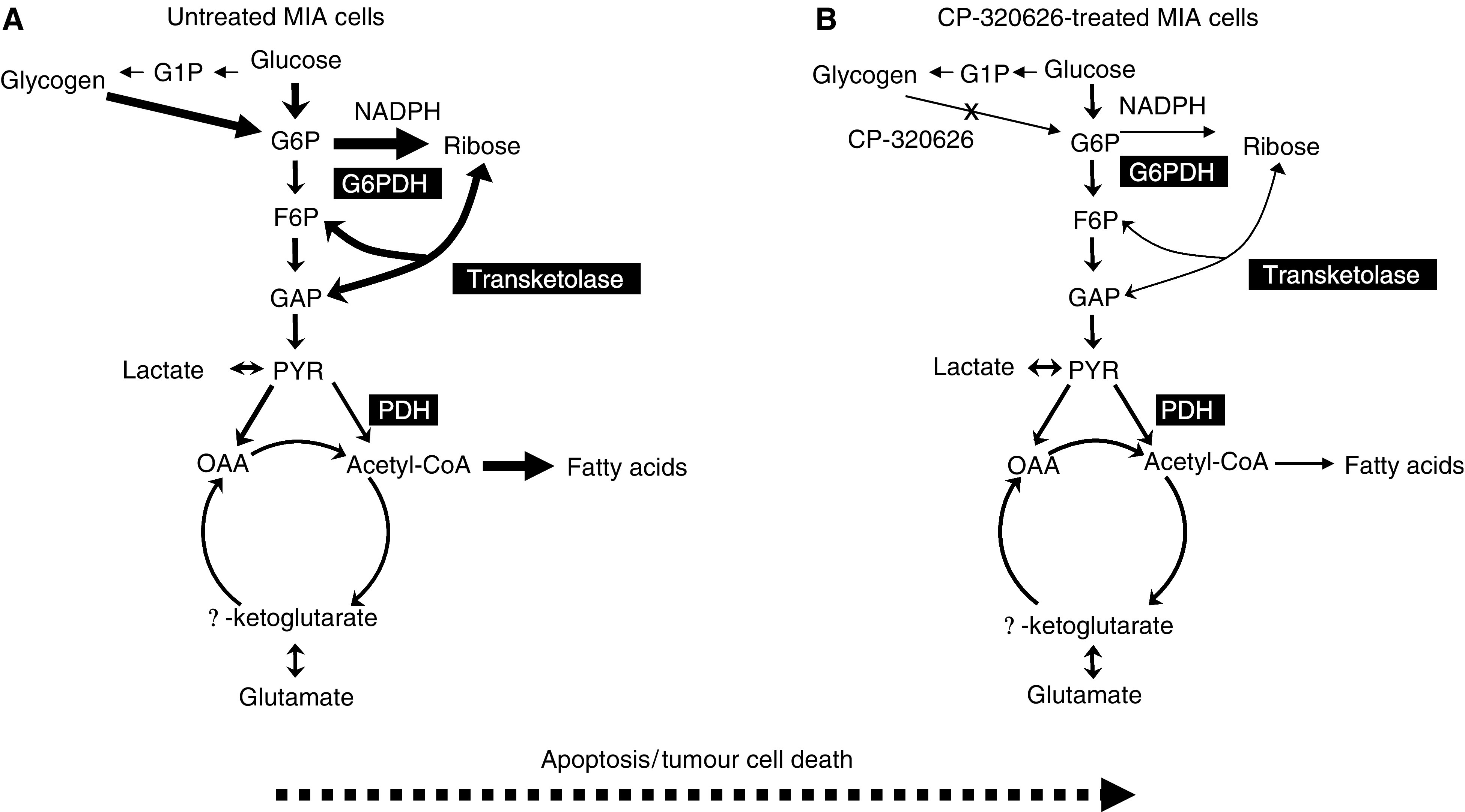
Metabolic profile changes associated with glycogen phosphorylase inhibitor treatment in MIA pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. MIA cells in the absence of CP-320626 utilise glucose as the major substrate for de novo nucleic acid and fatty acid synthesis as shown to the left (A). CP-3206262 limits glycogen breakdown as indicated on the panel to the right (B). As a result, tumour cells become less capable of synthesising nucleic acid ribose and fatty acids, which significantly limits their cycle progression and growth. One interesting feature of this metabolic profile is that it appears at lower concentrations of CP-320626 and precedes apoptosis formation. (G6P: glucose -6-P; G1P: glucose-1-P; F6P: fructose-6-P; GAP: glyceraldehyde-3-P; PYR: pyruvate; OAA: oxaloacetate).
