Figure 2.
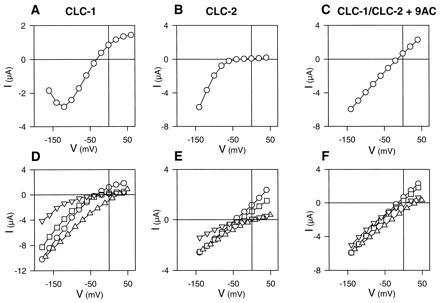
I–V relationships and ion selectivity of currents of oocytes expressing CLC-1 (A and D), CLC-2 (B and E), or both (C and F). (Upper A–C) Steady-state I–Vs in ND96 (104 mM Cl). (Lower D–F) Instantaneous I–Vs (open pore properties) with different anions in the bath. Measurements were performed in ND96 having 104 mM Cl (○), or in ND96 where 96 mM Cl were replaced by equal amounts of Br (□), glutamate (▵), or I (▿). This leaves 8 mM Cl in the medium. Data of one representative oocyte each are shown as a plot against the test potential. (A) Steady-state I–V of CLC-1. The current was measured at the end of a 100-ms test pulse. (B) Quasi-steady-state I–V of CLC-2 (measured at the end of a 6-s test pulse). (C) Steady-state I–V of CLC-1/CLC-2 heterooligomers (measured after treatment with 9-AC to block CLC-1 homooligomers). (D) Instantaneous I–V of CLC-1. Currents were extrapolated to the beginning of the test pulse by fitting the sum of two exponential functions. (E) Open-channel I–V of CLC-2. The oocyte was held at −140 mV until the current saturated before 200-ms test pulses were applied. (F) Instantaneous (equivalent to steady-state) I–V of the heterooligomer currents measured after 9-AC treatment.
