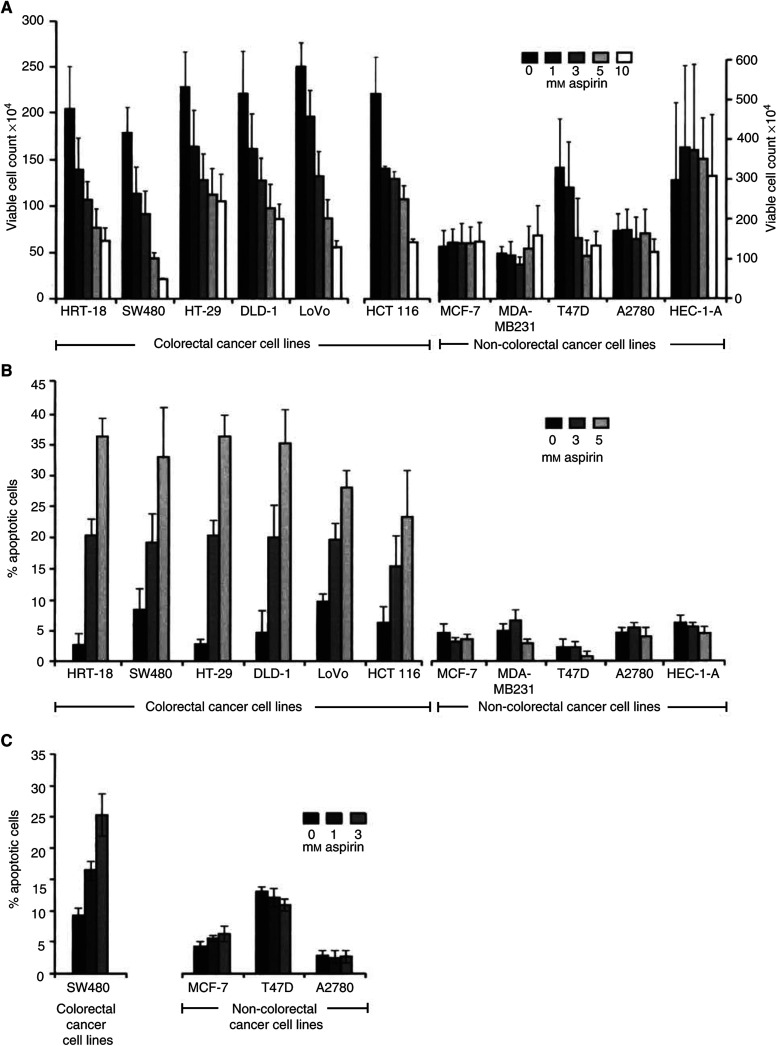
Figure 1.
Differential effect of aspirin on cell viability and apoptosis in CRC and non-CRC cell lines. Aspirin treatment (0–10 mM) for 24 h induces a concentration-dependent decrease in viable cell number (determined by haemocytometric counts) in all CRC cell lines, but there is no consistent change in the non-colorectal cancer cell lines (A). Annexin V binding assay is used to determine whether all CRC cell lines undergo apoptosis after aspirin treatment (0–5 mM) for 24 h, but there was no change in apoptosis in the non-CRC cell lines (B). Annexin V binding assay is used to determine whether the non-CRC cell lines are less susceptible to aspirin-induced apoptosis compared to the CRC cell line SW480 following treatment for 72 h with aspirin (0–3 mM) (C). The graphs represent three independent experiments and the bars on the graphs are standard error bars.