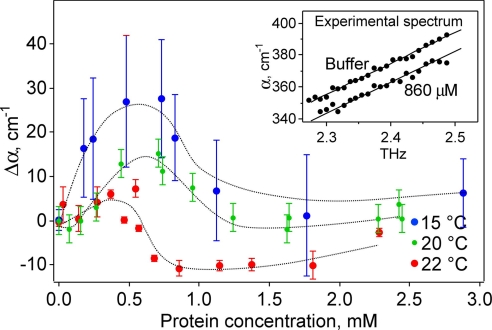
Fig. 1.
Difference in the THz absorption coefficient at 2.25 THz relative to bulk water plotted against concentration to 3 mM at 15°C, 20°C, and 22°C (more extensive averaging was done at 22°C because of the slightly smaller effect). The absorbance depends nonlinearly on concentration in this region. Note that the THz absorption for bulk water (zero point) increases with increasing temperature. (Inset) The frequency dependence of the absorption coefficient is linear between 2.25 and 2.55 THz (22°C: comparison of buffer and at a protein concentration of 860 μM).