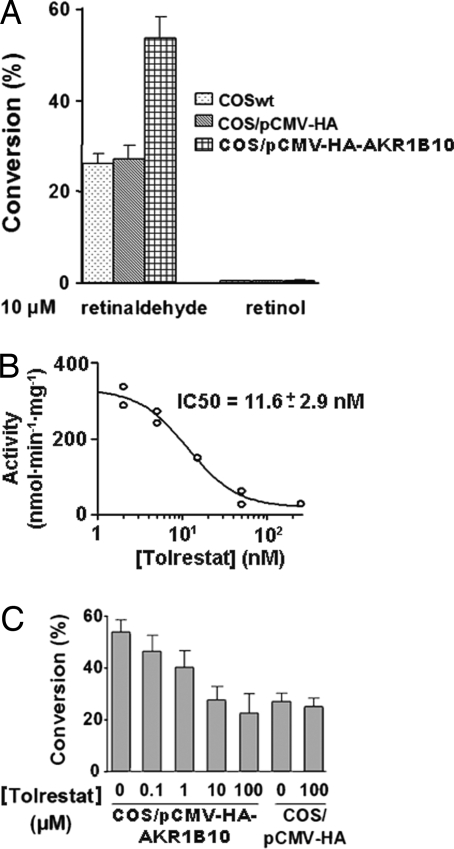
Fig. 1.
Retinaldehyde reductase activity of AKR1B10 and effect of tolrestat in vitro and in vivo. (A) Retinoid metabolism in COS-1 cells transiently expressing AKR1B10. Cellular retinoid content was measured by HPLC after incubating cells for 30 min with 10 μM retinaldehyde or 10 μM retinol. (B) Determination of tolrestat IC50 for retinaldehyde reductase activity of AKR1B10 using 0.5 μM retinaldehyde as a substrate. (C) Tolrestat inhibition of cellular AKR1B10 activity. COS-1 cells transfected with pCMV-HA-AKR1B10 were incubated with 10 μM all-trans-retinaldehyde and different concentrations of tolrestat. Data are expressed as the percentage of conversion of the retinoid taken up by cells (reduced retinaldehyde or oxidized retinol). Conversion for COS-1 cells transfected with empty vector (pCMV-HA) is shown as a control. Results are expressed as the mean ± SEM of at least three determinations.