Figure 1.
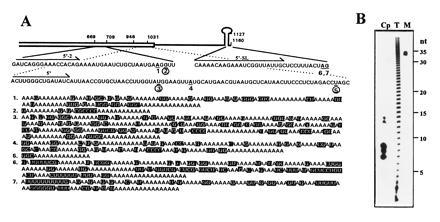
Posttranscriptional addition of poly(A)-rich sequences to spinach chloroplast psbA mRNA. (A) Nucleotide sequences and locations of the poly(A)-rich stretches that were PCR amplified from oligo(dT)-primed chloroplast cDNA. A schematic representation of the psbA RNA 3′ region is shown. The open box denotes the coding region. The single line represents the 3′ UTR in which the inverted repeats are symbolized by a stem–loop structure. The psbA gene is numbered according to Zurawski et al. (24), and the nucleotides where poly(A)-rich sequences had been added are numbered 1–7, underlined, and printed in boldface type. The poly(A)-rich addition sites coincident with endonucleolytic cleavage sites are circled (numbers 2, 3, and 5). The 3′ end of the mature psbA mRNA is located at nucleotides 1159A and 1160G, immediately following the inverted repeats that form the stem–loop structure (24); two of the poly(A)-rich addition sites, 6 and 7, were located at this position. The gene-specific primers are indicated by arrows. The poly(A)-rich stretches that are shown below, numbered 1–7, are those that were posttranscriptionally added to sites 1–7, respectively. The nucleotides that are not adenines are shaded. (B) Size of poly(A) tracts in chloroplast RNA. Total RNA from mature leaf cells (T) and purified chloroplast RNA (Cp) were labeled with [32P]pCp, followed by complete digestion of the RNAs with RNase T1 and RNase A. An end-labeled, 35-nt-long oligonucleotide was run in the same gel as a size marker (M).
