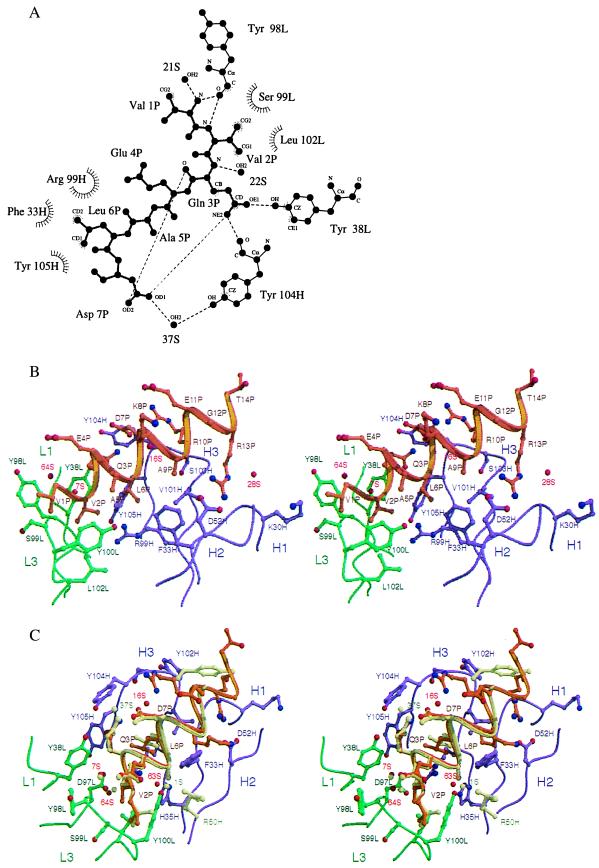
Figure 3.
Interactions between the α-helical peptide and the C219 binding site. (A) Two-dimensional ligplot (33) representation of the interactions between residues of the minimal NBD-epitope peptide (P), C219 heavy (H) and light chain (L) residues, and solvent molecules (S), as seen in molecule I. The residues that form van der Waals contacts with the peptide are depicted as labeled arcs with radial spokes pointing toward the peptide atoms with which they interact. C219 residues that form hydrogen bonds are shown in a ball-and-stick representation, and the hydrogen bonds are presented as dashed lines. Of all of the intrapeptide hydrogen bonds present in the structure, only the bonds between Gln 3P and Asp 7P are shown. (B) Stereoplot of the Fv-peptide interactions seen in molecule II. (C) Comparison of the bound NBD-epitope peptide in molecule I and II. In B and C, light (L) and heavy chain (H) residues and backbone positions of the scFv C219 are shown in green and magenta. Peptide backbone and side chains are shown in khaki for molecule I and in gold for molecule II. Positions of water molecules are indicated as red spheres. Different positions of binding site residues and water molecules in molecule I are also colored khaki. B and C were generated by using molscript (34) and raster3d (35).