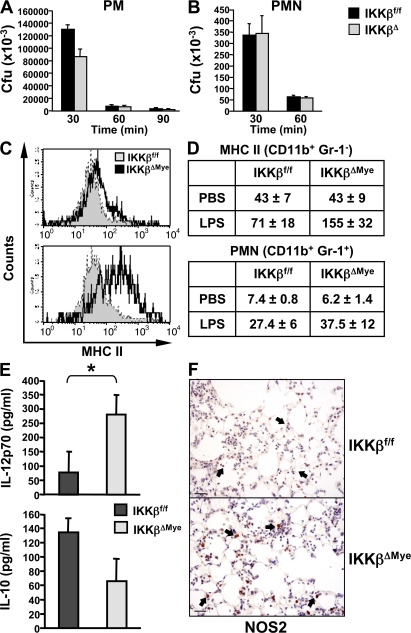
Figure 3.
IKKβ inhibits M1 macrophage activation in response to LPS in vivo. (A) Peritoneal macrophages (PM) and (B) neutrophils (PMN) were isolated from IKKβΔMye and IKKβf/f mice for in vitro killing assays with GBS (MOI of 5:1). (C) IKKβΔMye and IKKβf/f mice were challenged intranasally with 10 ng LPS in PBS. After 4 h, lungs were harvested and digested for FACS analysis of CD11b (myeloid), Gr-1 (PMN), and MHC class II expression. A representative histogram of MHC class II expression on CD11b+ Gr-1− alveolar macrophages is shown. (D) Tabulated data of mean fluorescence intensity for CD11b+ Gr-1− MHC class II+–activated macrophages in the lung and PMN recruitment as percentage of BAL cells from LPS-challenged mice (data are represented as mean ± SEM of n = 6). (E) In parallel experiments, IL-12 and IL-10 levels were measured in lung homogenates from LPS-challenged mice by ELISA. Data are represented as mean ± SEM (n = 8; *, P = 0.0381). (F) Immunohistochemical analysis of NOS2 expression in LPS-challenged mice. IKKβΔMye mice show increased expression of NOS2 in alveolar macrophages compared with IKKβf/f control mice (arrows). Representative panels are shown from n = 6 mice. Bar, 100 μm.