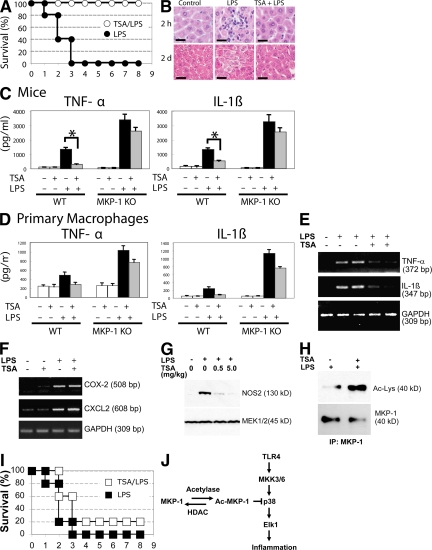
Figure 7.
HDAC inhibition decreases LPS induced mortality and inflammation in mice. (A) Mortality. Mice were injected with 1 mg/kg TSA daily for 5 d starting on day −2, injected with 50 mg/kg LPS on day 0, and their mortality was recorded each day after LPS treatment (n = 5; P < 0.00001 for LPS vs. LPS with TSA). (B) TSA decreases LPS-induced liver inflammation. Mice were injected with saline (control) or TSA each day starting on day −2, injected with LPS on day 0, and livers were harvested 2 h (top) or 2 d (bottom) after LPS, sectioned, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. (C) TSA decreases cytokine levels in serum. WT and MKP-1−/− mice were injected with TSA each day starting on day −2 and injected with LPS on day 0, and serum was collected 2 h after LPS treatment and analyzed by ELISA for TNF-α and IL-1β (n = 2 ± the SD; *, P < 0.05 ± the SD). (D) Cytokine from primary macrophages. Macrophages were prepared from WT and MKP-1−/− mice, stimulated with TSA, LPS, or both, and after 4 h TNF-α and IL-1β levels measured in the media by ELISA (n = 2 ± SD). (E) TSA suppresses cytokine RNA in vivo. Mice were injected with TSA each day starting on day −2, injected with LPS on day 0, and liver RNA was harvested 4 h after LPS treatment and analyzed by RT-PCR for TNF-α and IL-1β. Data are shown for two representative mice. (F) TSA slightly increases COX-2 and CXCL2 in vivo. Mice were injected with TSA and LPS as above, and liver RNA was harvested 4 h after LPS treatment and analyzed by RT-PCR for COX-2 and CXCL2 (n = 2). (G) Mouse NOS2 protein expression in liver. Mice were pretreated with increasing amounts of TSA for 4 h, and then treated with LPS for 16 h. Liver was harvested and immunoblotted with antibodies to NOS2 and MEK1. (H) MKP-1 is acetylated in mice. Mice were pretreated with TSA for 4 h, and then treated with LPS for 16 h as above. Liver lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibody to MKP-1 and immunoblotted with antibody to Ac-Lys or MKP-1. (I) MKP-1 mediates the protective effects of TSA after LPS. MKP-1 KO mice and their WT littermate controls were pretreated with TSA as above, and then injected with LPS 20 mg/kg, and their mortality was recorded (n = 5; P = 0.17 for LPS vs. LPS with TSA). (J) Proposed schematic of MKP-1 acetylation and regulation of innate immune signaling.