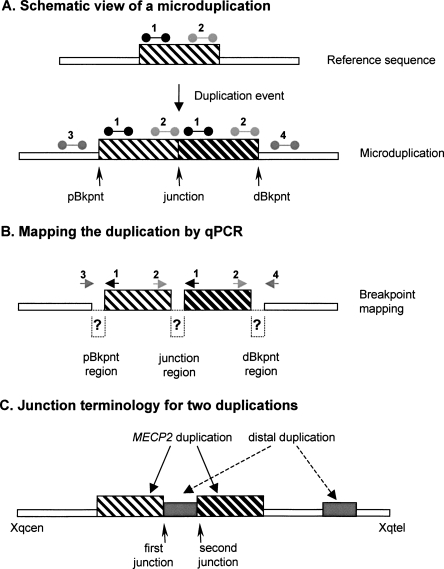
Figure 2.
Terminology used for Xq28 duplication breakpoint mapping and cloning. (A) Schematic of a duplicated segment in the genome. The reference genomic sequence (top), with the region that is duplicated in the lower scheme, is indicated as a thin-striped box. qPCR primer pairs used for duplication size mapping are shown above this box at the proximal (1) and distal (2) side of this region. When duplicated in tandem (bottom), the proximal position where the duplication starts is called the proximal breakpoint (pBkpnt). Similarly, the most distal position where the duplication stops is called the distal breakpoint (dBkpnt). The position where the first copy is followed by the second one is the junction. In qPCR analysis, primer pairs 1 as well as 2 will yield a double dose while the primer pairs for 3 and 4 will give a single copy (relative to the reference genome). (B) For mapping purposes the pBkpnt and dBkpnt regions lie in between the last “normal” forward (3) and the first “duplicated” reverse primer (1), and the last “duplicated” forward (2) and the first “normal” reverse primer (4), respectively. To amplify over the junction, the first “duplicated” forward primer of the proximal breakpoint (1) was combined with the last “duplicated” reverse primer of the distal breakpoint (2). The region in between both primer pairs is called the junction region. Normal sequences are represented by thin open boxes; duplicated sequence by thin-striped and thick-striped boxes, which represent the first and second copy, respectively. (C) Junction terminology for the two duplications.