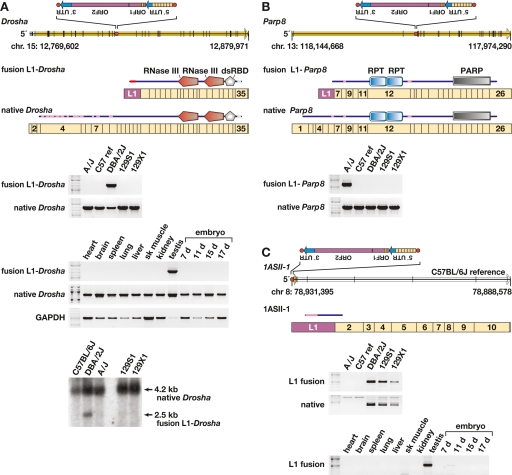
Figure 5.
Transcriptional variation due to L1 variants. (A) (Top) Genomic structure of Drosha (Rnasen) on mouse chromosome 15 (Feb. 2006 assembly), presented left to right (5′ to 3′), with exons (black vertical lines); ORF (yellow arrow); intronic, antisense L1 polymorphism including its 5′ UTR, ORF-1 and ORF-2, and 3′ UTR (inset); and L1 target site (red dot) as indicated. The L1 target-site sequence, presented in the orientation of Drosha, is 5′-TCGCGCTTTGGCTTCTTT. Also presented are fusion L1-Drosha and native Drosha spliced, poly(A)+ transcript structures including relative lengths and numbers of Drosha (tan rectangle) and antisense L1 (purple) exons. Above each transcript is a schematic indicating predicted translation products (from start to stop codons) including RNaseIII and double-stranded RNA-binding domains, and low complexity (pink) and coiled-coil (light blue) domains (annotated by SMART program). (Middle) RT–PCR assay for fusion L1-Drosha and native transcripts in total RNA from five mouse strain testes and assay for fusion L1-Drosha transcript from Balb/cJ tissues as indicated. (Bottom) Northern blot probed for Drosha transcripts, indicating fusion L1-Drosha expression only in DBA/2J mice. (B) (Top) Genomic structure of Parp8 on the minus strand of chromosome 13, including genomic features as in A. The L1 target site sequence, in the orientation of Parp8, is 5′-CCTCCGACGTTAAAG. Also presented are fusion L1-Parp8 and native Parp8 spliced, poly(A)+ transcripts, including relative exon lengths (tan rectangles), numbers, and the antisense L1 exon (purple). Above each transcript is a schematic indicating predicted translation products including internally repeated (RPT) and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) catalytic domains, and low-complexity (pink) domains (SMART). (Bottom) RT–PCR assay for fusion L1-Parp8 and native transcripts. (C) (Top) Genomic and transcript structures for 1ASII-1, a novel, spliced transcript initiated by a polymorphic L1 on the minus strand of chromosome 8, including genomic features as in A. The L1 target-site sequence, presented in the sense orientation of 1ASII-1, is 5′-GACGTATAGACAAGAA. Also presented is poly(A)+ transcript 1ASII-1 (open arrow), including its relative exon lengths (tan rectangles), numbers and the antisense L1 exon (purple). Above it is a schematic indicating predicted translation products with low complexity (pink) domain as indicated (SMART program). (Bottom) RT-PCR assay for fusion L1-1ASII-1 and native (lacking the L1 exon) transcripts and for the fusion L1 transcript in Balb/cJ tissues as indicated. This L1 variant initiates transcription in testis and 11-d embryo, only in strains containing the variant.